Fast robust automated brain extraction
- PMID: 12391568
- PMCID: PMC6871816
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10062
Fast robust automated brain extraction
Abstract
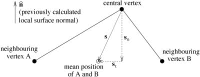
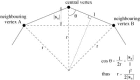
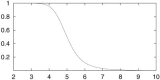
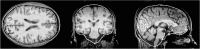
An automated method for segmenting magnetic resonance head images into brain and non-brain has been developed. It is very robust and accurate and has been tested on thousands of data sets from a wide variety of scanners and taken with a wide variety of MR sequences. The method, Brain Extraction Tool (BET), uses a deformable model that evolves to fit the brain's surface by the application of a set of locally adaptive model forces. The method is very fast and requires no preregistration or other pre-processing before being applied. We describe the new method and give examples of results and the results of extensive quantitative testing against "gold-standard" hand segmentations, and two other popular automated methods.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
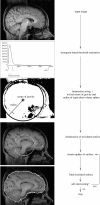
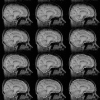
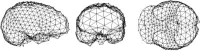
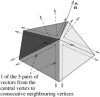
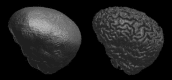
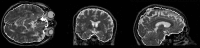

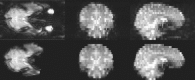
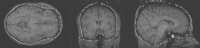
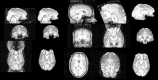
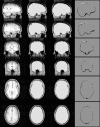
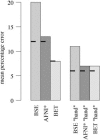
References
-
- Atkins M, Mackiewich B (1998): Fully automatic segmentation of the brain in MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17: 98–107. - PubMed
-
- Bomans M, Höhne K‐H, Tiede U, Riemer M (1990): 3‐D Segmentation of MR images of the head for 3‐D display. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 9: 177–183. - PubMed
-
- Brummer M, Mersereau R, Eisner R, Lewine R (1993): Automatic detection of brain contours in MRI data sets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 12: 153–166. - PubMed
-
- Cox R. AFNI software . Online: http://afni.nimh.nih.gov.
-
- Dale A, Fischl B, Sereno M (1999): Cortical surface‐based analysis I: segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9: 179–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

