Collagen deposition in HIV-1 infected lymphatic tissues and T cell homeostasis
- PMID: 12393849
- PMCID: PMC150803
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16413
Collagen deposition in HIV-1 infected lymphatic tissues and T cell homeostasis
Abstract
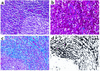
Lymphatic tissues (LTs) are structurally organized to promote interaction between antigens, chemokines, growth factors, and lymphocytes to generate an immunologic response and maintain normal-sized populations of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. Inflammation and tissue remodeling that accompany local innate and adaptive immune responses to HIV-1 replication cause damage to the LT architecture. As a result, normal populations of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells cannot be supported and antigen-lymphocyte interactions are impaired. This conclusion is supported herein following LT sampling before and during anti-HIV therapy in persons with acute, chronic, and late-stage HIV-1 infection. Among seven individuals treated with anti-retroviral therapy (ART) and four individuals deferring therapy we found evidence of significant paracortical T cell zone damage associated with deposition of collagen, the extent of which was inversely correlated with both the size of the LT CD4(+) T cell population and the change in peripheral CD4(+) T cell count with anti-HIV therapy. The HIV-1-associated inflammatory changes and scarring in LT both limit the ability of the tissue to support and reestablish normal-sized populations of CD4(+) T cells and suggest a novel mechanism of T cell depletion that may explain the failure of ART to significantly increase CD4(+) T cell populations in some HIV-1-infected persons.
Figures


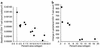
References
-
- Kaldjian EP, Gretz JE, Anderson AO, Shi Y, Shaw S. Spatial and molecular organization of lymph node T cell cortex: a labyrinthine cavity bounded by an epithelium-like monolayer of fibroblastic reticular cells anchored to basement membrane-like extracellular matrix. Int Immunol. 2001;13:1243–1253. - PubMed
-
- Gretz JE, Kaldjian EP, Anderson AO, Shaw S. Sophisticated strategies for information encounter in the lymph node: the reticular network as a conduit of soluble information and a highway for cell traffic. J Immunol. 1996;157:495–499. - PubMed
-
- Gretz JE, Norbury CC, Anderson AO, Proudfoot AE, Shaw S. Lymph-borne chemokines and other low molecular weight molecules reach high endothelial venules via specialized conduits while a functional barrier limits access to the lymphocyte microenvironments in lymph node cortex. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1425–1440. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

