Investigation of bioterrorism-related anthrax, United States, 2001: epidemiologic findings
- PMID: 12396909
- PMCID: PMC2730292
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0810.020353
Investigation of bioterrorism-related anthrax, United States, 2001: epidemiologic findings
Abstract
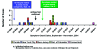
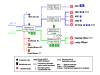
In October 2001, the first inhalational anthrax case in the United States since 1976 was identified in a media company worker in Florida. A national investigation was initiated to identify additional cases and determine possible exposures to Bacillus anthracis. Surveillance was enhanced through health-care facilities, laboratories, and other means to identify cases, which were defined as clinically compatible illness with laboratory-confirmed B. anthracis infection. From October 4 to November 20, 2001, 22 cases of anthrax (11 inhalational, 11 cutaneous) were identified; 5 of the inhalational cases were fatal. Twenty (91%) case-patients were either mail handlers or were exposed to worksites where contaminated mail was processed or received. B. anthracis isolates from four powder-containing envelopes, 17 specimens from patients, and 106 environmental samples were indistinguishable by molecular subtyping. Illness and death occurred not only at targeted worksites, but also along the path of mail and in other settings. Continued vigilance for cases is needed among health-care providers and members of the public health and law enforcement communities.
Figures
References
-
- Brachman P, Kaufmann A. Anthrax. In: Evans A, Brachman P, editors. Bacterial infections of humans. New York: Plenum Medical Book Company; 1998. p. 95–107.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Human anthrax associated with an epizootic among livestock—North Dakota, 2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:677–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
