Specific, sensitive, and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human immunoglobulin G antibodies to anthrax toxin protective antigen
- PMID: 12396924
- PMCID: PMC2730307
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0810.020380
Specific, sensitive, and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human immunoglobulin G antibodies to anthrax toxin protective antigen
Abstract
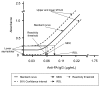
The bioterrorism-associated human anthrax epidemic in the fall of 2001 highlighted the need for a sensitive, reproducible, and specific laboratory test for the confirmatory diagnosis of human anthrax. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention developed, optimized, and rapidly qualified an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies to Bacillus anthracis protective antigen (PA) in human serum. The qualified ELISA had a minimum detection limit of 0.06 micro g/mL, a reliable lower limit of detection of 0.09 micro g/mL, and a lower limit of quantification in undiluted serum specimens of 3.0 micro g/mL anti-PA IgG. The diagnostic sensitivity of the assay was 97.8%, and the diagnostic specificity was 97.6%. A competitive inhibition anti-PA IgG ELISA was also developed to enhance diagnostic specificity to 100%. The anti-PA ELISAs proved valuable for the confirmation of cases of cutaneous and inhalational anthrax and evaluation of patients in whom the diagnosis of anthrax was being considered.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Human anthrax associated with an epizootic among livestock—North Dakota, 2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50:677–80. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: cutaneous anthrax in a laboratory worker—Texas, 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:482. - PubMed
-
- Leppla SH. Purification and characterization of adenylyl cyclase from Bacillus anthracis. In: Johnson A, Corbin JD. Methods in enzymology. Vol 195. San Diego: Academic Press;1991. p. 153–68. - PubMed
-
- Reimer CB, Smith SJ, Wells TW, Nakamura RM, Keitges PW, Ritchie RF, et al. Collaborative calibration of the U.S. National and the College of American Pathologists reference preparation for specific serum proteins. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982;77:12–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
