Cell-surface proteolysis, growth factor activation and intercellular communication in the progression of melanoma
- PMID: 12398996
- PMCID: PMC7129480
- DOI: 10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00196-2
Cell-surface proteolysis, growth factor activation and intercellular communication in the progression of melanoma
Abstract
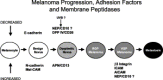
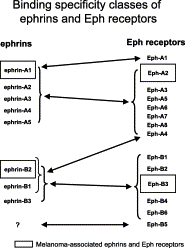
Normal skin architecture and melanocyte function is maintained by a dynamic interplay between the melanocytes themselves, the epithelial cells between which they are interspersed, and their microenvironment. The microenvironment consists of the extracellular matrix, fibroblasts, migratory immune cells, and neural elements supported by a vascular network, all within a milieu of cytokines, growth factors, and bioactive peptides as well as proteolytic enzymes. Cells interact with the microenvironment via complex autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Proteolytic enzymes in melanoma may activate or release growth factors from the microenvironment or act directly on the microenvironment itself, thereby facilitating angiogenesis or tumor cell migration. This review summarizes recent findings regarding the expression, structure and function of proteolytic enzymes at or near the cell surface in cell-cell and cell-stroma interactions during melanoma progression. Cell-surface (membrane) peptidases are a multi-functional group of ectoenzymes that have been implicated in the control of growth and differentiation of many cellular systems. The potential, but yet speculative, role of other membrane-bound molecules, such as multifunctional surface proteins with adhesion and protease activity (ADAM gene family) or the ephrin/Eph receptor protein kinases in the pathogenesis of melanoma are discussed.
Figures



References
-
- Kamb A, Herlyn M. Malignant melanoma. In: Scriver C.R, Beaudet A.L, Sly W.S, Valle D, editors. The Metabolc and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. eighth ed. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001. pp. 967–977.
-
- Herlyn M, Satyamoorthy K. Molecular biology of cutaneous melanoma. In: DeVita V.T Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg S.A, editors. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. sixth ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2001. pp. 2003–2012.
-
- Sherr C.J. The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3689–3695. - PubMed
-
- Piepkorn M. Melanoma genetics: an update with focus on the CDKN2A(p16)/ARF tumor suppressors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000;42:705–722. - PubMed
-
- Park C.C, Bissell M.J, Barcellos-Hoff M.H. The influence of the microenvironment on the malignant phenotype. Mol. Med. Today. 2000;6:324–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

