The iddm4 locus segregates with diabetes susceptibility in congenic WF.iddm4 rats
- PMID: 12401717
- PMCID: PMC4034451
- DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.51.11.3254
The iddm4 locus segregates with diabetes susceptibility in congenic WF.iddm4 rats
Abstract
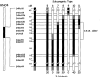
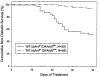
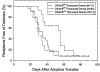
Viral antibody-free BBDR and WF rats never develop spontaneous diabetes. BBDR rats, however, develop autoimmune diabetes after perturbation of the immune system, e.g., by viral infection. We previously identified a disease-susceptibility locus in the BBDR rat, iddm4, which is associated with the development of autoimmune diabetes after treatment with polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid and an antibody that depletes ART2(+) regulatory cells. We have now developed lines of congenic WF.iddm4 rats and report that in an intercross of N5 generation WF.iddm4 rats, approximately 70% of animals either homozygous or heterozygous for the BBDR origin allele of iddm4 became hyperglycemic after treatment to induce diabetes. Fewer than 20% of rats expressing the WF origin allele of iddm4 became diabetic. Testing the progeny of various recombinant N5 WF.iddm4 congenic rats for susceptibility to diabetes suggests that iddm4 is centered on a small segment of chromosome 4 bounded by the proximal marker D4Rat135 and the distal marker D4Got51, an interval of <2.8 cM. The allele at iddm4 has 79% sensitivity and 80% specificity in prediction of diabetes in rats that are segregating for this locus. These characteristics suggest that iddm4 is one of the most powerful non-major histocompatibility complex determinants of susceptibility to autoimmune diabetes described to date.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The rat diabetes susceptibility locus Iddm4 and at least one additional gene are required for autoimmune diabetes induced by viral infection.Diabetes. 2005 Apr;54(4):1233-7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.4.1233. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 15793267 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes-prone and diabetes-resistant BB rats share a common major diabetes susceptibility locus, iddm4: additional evidence for a "universal autoimmunity locus" on rat chromosome 4.Diabetes. 1999 Nov;48(11):2138-44. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.11.2138. Diabetes. 1999. PMID: 10535446
-
Refinement of the Iddm4 diabetes susceptibility locus reveals TCRVbeta4 as a candidate gene.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Apr;1103:128-31. doi: 10.1196/annals.1394.020. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17376830
-
Rat models of type 1 diabetes: genetics, environment, and autoimmunity.ILAR J. 2004;45(3):278-91. doi: 10.1093/ilar.45.3.278. ILAR J. 2004. PMID: 15229375 Review.
-
Autoimmune disorders in diabetes.Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1986;15:281-305. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1986. PMID: 3082114 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of type 1 diabetes in the rat with an allele-specific anti-T-cell receptor antibody: Vβ13 as a therapeutic target and biomarker.Diabetes. 2012 May;61(5):1160-8. doi: 10.2337/db11-0867. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22368175 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantigen-induced focusing of Vβ13+ T cells precedes onset of autoimmune diabetes in the LEW.1WR1 rat.Diabetes. 2014 Feb;63(2):596-604. doi: 10.2337/db13-0462. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24150607 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Role for the Type I Interferon Receptor in Virus-Induced Autoimmune Diabetes in Rats.Diabetes. 2017 Jan;66(1):145-157. doi: 10.2337/db16-0462. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 27999109 Free PMC article.
-
The Missing Heritability in T1D and Potential New Targets for Prevention.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:737485. doi: 10.1155/2013/737485. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23691517 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mapping of rat Iddm4 to segments on HSA7 and MMU6.Mamm Genome. 2004 Jan;15(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00335-003-3023-z. Mamm Genome. 2004. PMID: 14727142
References
-
- Pietropaolo M, Trucco M. Major histocompatibility locus and other genes that determine the risk of development of type 1 diabetes mellitus. In: LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM, editors. Diabetes Mellitus: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2000. pp. 399–410.
-
- Dahlman I, Eaves IA, Kosoy R, Morrison VA, Heward J, Gough SCL, Allahabadia A, Franklyn JA, Tuomilehto J, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Cucca F, Giya C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Stevens H, Carr P, Nutland S, McKinney P, Shield JP, Wang W, Cordell HJ, Walker N, Todd JA, Concarmon P. Parameters for reliable results in genetic association studies in common disease. Nat Genet. 2002;30:149–150. - PubMed
-
- Leiter E. Genetics and immunogenetics of NOD mice and related strains. In: Leiter E, Atkinson M, editors. NOD Mice and Related Strains: Research Applications in Diabetes, AIDS, Cancer, and Other Diseases. R.G. Landes; Austin, TX: 1998. pp. 37–69.
-
- Mordes JP, BorteZI K, Groen H, Gubersld DL, Rossini AA, Greiner DL. Autoimmune diabetes mellitus in the BB rat. In: Sima AAF, Shafrir E, editors. Animal Models of Diabetes: A primer. Harwood Academic; Amsterdam: 2001. pp. 1–41.
-
- Crisé L, Mordes JP, Rossini AA. Autoimmune diabetes mellitus in the BB rat (Review Article) Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992;8:4–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

