Down-regulation of Delta by proteolytic processing
- PMID: 12403816
- PMCID: PMC2173041
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200203117
Down-regulation of Delta by proteolytic processing
Abstract
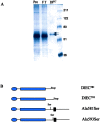
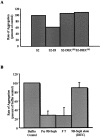
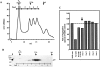
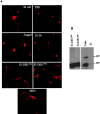
Notch signaling regulates cell fate decisions during development through local cell interactions. Signaling is triggered by the interaction of the Notch receptor with its transmembrane ligands expressed on adjacent cells. Recent studies suggest that Delta is cleaved to release an extracellular fragment, DlEC, by a mechanism that involves the activity of the metalloprotease Kuzbanian; however, the functional significance of that cleavage remains controversial. Using independent functional assays in vitro and in vivo, we examined the biological activity of purified soluble Delta forms and conclude that Delta cleavage is an important down-regulating event in Notch signaling. The data support a model whereby Delta inactivation is essential for providing the critical ligand/receptor expression differential between neighboring cells in order to distinguish the signaling versus the receiving partner.
Figures

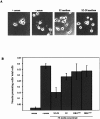


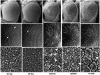

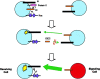
References
-
- Al-Atia, G.R., P. Fruscoloni, M. Jacobs-Lorena. 1985. Translational regulation of mRNAs for ribosomal proteins during early Drosophila development. Biochemistry. 24:5798–5803. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., K. Matsuno, and M.E. Fortini. 1995. Notch signaling. Science. 268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S., M.D. Rand, and R.J. Lake. 1999. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Brand, A.H., and N. Perrimon. 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 118:401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

