Distinct claudins and associated PDZ proteins form different autotypic tight junctions in myelinating Schwann cells
- PMID: 12403818
- PMCID: PMC2173042
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200207050
Distinct claudins and associated PDZ proteins form different autotypic tight junctions in myelinating Schwann cells
Abstract
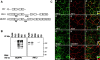
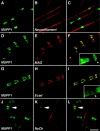
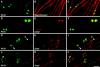
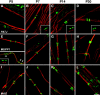
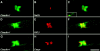
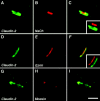
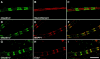
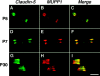
The apposed membranes of myelinating Schwann cells are joined by several types of junctional specializations known as autotypic or reflexive junctions. These include tight, gap, and adherens junctions, all of which are found in regions of noncompact myelin: the paranodal loops, incisures of Schmidt-Lanterman, and mesaxons. The molecular components of autotypic tight junctions have not been established. Here we report that two homologues of Discs Lost-multi PDZ domain protein (MUPP)1, and Pals-associated tight junction protein (PATJ), are differentially localized in myelinating Schwann cells and associated with different claudins. PATJ is mainly found at the paranodal loops, where it colocalized with claudin-1. MUPP1 and claudin-5 colocalized in the incisures, and the COOH-terminal region of claudin-5 interacts with MUPP1 in a PSD-95/Disc Large/zona occludens (ZO)-1 (PDZ)-dependent manner. In developing nerves, claudin-5 and MUPP1 appear together in incisures during the first postnatal week, suggesting that they coassemble during myelination. Finally, we show that the incisures also contain four other PDZ proteins that are found in epithelial tight junctions, including three membrane-associated guanylate-kinase proteins (membrane-associated guanylate-kinase inverted-2, ZO-1, and ZO-2) and the adaptor protein Par-3. The presence of these different tight junction proteins in regions of noncompact myelin may be required to maintain the intricate cytoarchitecture of myelinating Schwann cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tricellulin is expressed in autotypic tight junctions of peripheral myelinating Schwann cells.J Histochem Cytochem. 2010 Dec;58(12):1067-73. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2010.956326. J Histochem Cytochem. 2010. PMID: 21097846 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junction proteins in human Schwann cell autotypic junctions.J Histochem Cytochem. 2009 Jun;57(6):523-9. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2009.951681. Epub 2009 Jan 19. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009. PMID: 19153196 Free PMC article.
-
Tight junction contact events and temporary gap junctions in the sciatic nerve fibres of the chicken during Wallerian degeneration and subsequent regeneration.J Neurocytol. 1982 Oct;11(5):839-58. doi: 10.1007/BF01153522. J Neurocytol. 1982. PMID: 7143029
-
Ruffles and spikes: Control of tight junction morphology and permeability by claudins.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Sep 1;1862(9):183339. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183339. Epub 2020 May 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32389670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular junctions of myelinated nerves (Review).Mol Membr Biol. 2002 Apr-Jun;19(2):95-101. doi: 10.1080/09687680210130009. Mol Membr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12126235 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic disruption of Pten in a novel mouse model of tomaculous neuropathy.EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Jun;4(6):486-99. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201200227. Epub 2012 Apr 4. EMBO Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22488882 Free PMC article.
-
SCN2A-linked myelination deficits and synaptic plasticity alterations drive auditory processing disorders in ASD.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 28:rs.3.rs-4925935. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4925935/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 2;16(1):7109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62494-3. PMID: 39257993 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Tight junctions in Schwann cells of peripheral myelinated axons: a lesson from claudin-19-deficient mice.J Cell Biol. 2005 May 9;169(3):527-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501154. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15883201 Free PMC article.
-
Dichloromethane Extracts of Geranium Koreanum Kom. Alleviates Esophagus Damage in Acute Reflux Esophagitis-Induced Rats by Anti-Inflammatory Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 16;19(11):3622. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113622. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30453554 Free PMC article.
-
Laurate permeabilizes the paracellular pathway for small molecules in the intestinal epithelial cell model HT-29/B6 via opening the tight junctions by reversible relocation of claudin-5. [Corrected].Pharm Res. 2014 Sep;31(9):2539-48. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1350-2. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24633418
References
-
- Baumgartner, S., J.T. Littleton, K. Broadie, M.A. Bhat, R. Harbecke, J.A. Lengyel, R. Chiquet-Ehrismann, A. Prokop, and H.J. Bellen. 1996. A Drosophila neurexin is required for septate junction and blood-nerve barrier formation and function. Cell. 87:1059–1068. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni, G., O.M. Martinez-Estrada, F. Orsenigo, M. Cordenonsi, S. Citi, and E. Dejana. 2000. Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J. Biol. Chem. 275:20520–20526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

