Occurrence of mycobacteria in water treatment lines and in water distribution systems
- PMID: 12406720
- PMCID: PMC129932
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.11.5318-5325.2002
Occurrence of mycobacteria in water treatment lines and in water distribution systems
Abstract
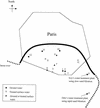
The frequency of recovery of atypical mycobacteria was estimated in two treatment plants providing drinking water to Paris, France, at some intermediate stages of treatment. The two plants use two different filtration processes, rapid and slow sand filtration. Our results suggest that slow sand filtration is more efficient for removing mycobacteria than rapid sand filtration. In addition, our results show that mycobacteria can colonize and grow on granular activated carbon and are able to enter distribution systems. We also investigated the frequency of recovery of mycobacteria in the water distribution system of Paris (outside buildings). The mycobacterial species isolated from the Paris drinking water distribution system are different from those isolated from the water leaving the treatment plants. Saprophytic mycobacteria (present in 41.3% of positive samples), potentially pathogenic mycobacteria (16.3%), and unidentifiable mycobacteria (54.8%) were isolated from 12 sites within the Paris water distribution system. Mycobacterium gordonae was preferentially recovered from treated surface water, whereas Mycobacterium nonchromogenicum was preferentially recovered from groundwater. No significant correlations were found among the presence of mycobacteria, the origin of water, and water temperature.
Figures

References
-
- Astagneau, P., N. Desplaces, V. Vincent, V. Chicheportiche, A. Botherel, S. Maugat, K. Lebascle, P. Leonard, J. Desenclos, J. Grosset, J. Ziza, and G. Brucker. 2001. Mycobacterium xenopi spinal infections after discovertebral surgery: investigation and screening of a large outbreak. Lancet 358:747-751. - PubMed
-
- Bolan, G., A. L. Reingold, L. A. Carson, V. A. Silcox, C. L. Woodley, P. S. Hayes, A. W. Hightower, L. McFarland, J. W. D. Brown, and N. J. Petersen. 1985. Infections with Mycobacterium chelonei in patients receiving dialysis and using processed hemodialyzers. J. Infect. Dis. 152:1013-1019. - PubMed
-
- Campagnaro, R. L., H. Teichtahl, and B. Dwyer. 1994. A pseudoepidemic of Mycobacterium chelonae: contamination of a bronchoscope and autocleaner. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 24:693-695. - PubMed
-
- Chauret, C., N. Armstrong, J. Fisher, R. Sharma, S. Springthorpe, and S. Sattar. 1995. Correlating Cryptosporidium and Giardia with microbial indicators. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 87:76-84.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

