The Usher syndrome proteins cadherin 23 and harmonin form a complex by means of PDZ-domain interactions
- PMID: 12407180
- PMCID: PMC137525
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.232579599
The Usher syndrome proteins cadherin 23 and harmonin form a complex by means of PDZ-domain interactions
Abstract
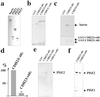
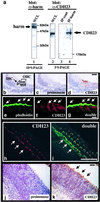
Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1) patients suffer from sensorineuronal deafness, vestibular dysfunction, and visual impairment. Several genetic loci have been linked to USH1, and four of the relevant genes have been identified. They encode the unconventional myosin VIIa, the PDZ-domain protein harmonin, and the putative adhesion receptors cadherin 23 (CDH23) and protocadherin 15 (PCDH15). We show here that CDH23 and harmonin form a protein complex. Two PDZ domains in harmonin interact with two complementary binding surfaces in the CDH23 cytoplasmic domain. One of the binding surfaces is disrupted by sequences encoded by an alternatively spliced CDH23 exon that is expressed in the ear, but not the retina. In the ear, CDH23 and harmonin are expressed in the stereocilia of hair cells, and in the retina within the photoreceptor cell layer. Because CDH23-deficient mice have splayed stereocilia, our data suggest that CDH23 and harmonin are part of a transmembrane complex that connects stereocilia into a bundle. Defects in the formation of this complex are predicted to disrupt stereocilia bundles and cause deafness in USH1 patients.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interactions in the network of Usher syndrome type 1 proteins.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Feb 1;14(3):347-56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi031. Epub 2004 Dec 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15590703
-
Photoreceptor expression of the Usher syndrome type 1 protein protocadherin 15 (USH1F) and its interaction with the scaffold protein harmonin (USH1C).Mol Vis. 2005 May 12;11:347-55. Mol Vis. 2005. PMID: 15928608
-
Molecular basis of human Usher syndrome: deciphering the meshes of the Usher protein network provides insights into the pathomechanisms of the Usher disease.Exp Eye Res. 2006 Jul;83(1):97-119. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.11.010. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16545802 Review.
-
A core cochlear phenotype in USH1 mouse mutants implicates fibrous links of the hair bundle in its cohesion, orientation and differential growth.Development. 2008 Apr;135(8):1427-37. doi: 10.1242/dev.012922. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Development. 2008. PMID: 18339676
-
Usher I syndrome: unravelling the mechanisms that underlie the cohesion of the growing hair bundle in inner ear sensory cells.J Cell Sci. 2005 Oct 15;118(Pt 20):4593-603. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02636. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16219682 Review.
Cited by
-
Rbm24 regulates inner-ear-specific alternative splicing and is essential for maintaining auditory and motor coordination.RNA Biol. 2021 Apr;18(4):468-480. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1817265. Epub 2020 Sep 20. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32887533 Free PMC article.
-
PDZD7-MYO7A complex identified in enriched stereocilia membranes.Elife. 2016 Aug 15;5:e18312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18312. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27525485 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling adhesion to actin bundles in the inner ear. Novel functions for novel cadherins.EMBO Rep. 2003 Mar;4(3):244-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.embor775. EMBO Rep. 2003. PMID: 12634839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Grxcr1 Promotes Hair Bundle Development by Destabilizing the Physical Interaction between Harmonin and Sans Usher Syndrome Proteins.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 30;25(5):1281-1291.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.005. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30380418 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of USH1C and DFNB18: phenotypic and molecular analyses of two new spontaneous mutations of the Ush1c gene.Hum Mol Genet. 2003 Dec 1;12(23):3075-86. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg332. Epub 2003 Sep 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2003. PMID: 14519688 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

