"Actinobaculum massiliae," a new species causing chronic urinary tract infection
- PMID: 12409355
- PMCID: PMC139656
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.3938-3941.2002
"Actinobaculum massiliae," a new species causing chronic urinary tract infection
Abstract
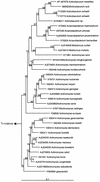
We report on a new Actinobaculum species, "Actinobaculum massiliae," isolated from the urine of an elderly woman with recurrent cystitis. Its phenotypic pattern was similar to those of both of the other Actinobaculum species described to date. On 16S rRNA sequencing, the Marseille isolate shared 95% homology with Actinobaculum suis, 92 to 93% homology with Actinobaculum schaalii, 91 to 92% homology with Arcanobacterium spp., and 87 to 90% homology with Actinomyces species. A bootstrap value of 99% supports the node separating the Actinobaculum sp. from its closest neighbor (A. suis). In conclusion, on the basis of phenotypic, genotypic, and phylogenetic assessments, we show that the Marseille isolate is a previously unrecognized organism within the Actinobaculum genus, and we propose placement of the organism in the taxon "Actinobaculum massiliae."
Figures
References
-
- Felsenstein, J. 1989. PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package. Cladistics 5:164-166.
-
- Lawson, P. A., E. Falsen, E. Akervall, P. Vandamme, and M. D. Collins. 1997. Characterization of some Actinomyces-like isolates from human clinical specimens: reclassification of Actinomyces suis (Soltys and Spratling) as Actinobaculum schaalii comb. nov. and description of Actinobaculum schaalii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:899-903. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig, W., G. Kirchhof, M. Weizenzgger, and N. Weiss. 1992. Phylogenetic evidence for transfer of Eubacterium suis to the genus Actinomyces as Actinomyces suis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42:161-165. - PubMed
-
- Miller, L., and T. Berger. 1985. Bacterial identification by gas chromatography of whole cell fatty acid, p. 228-241. Hewlett-Packard Co., Palo Alto, Calif.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

