Use of epitope mapping to identify a PCR template for protein amplification and detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein D
- PMID: 12409372
- PMCID: PMC139723
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4045-4050.2002
Use of epitope mapping to identify a PCR template for protein amplification and detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein D
Abstract
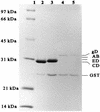
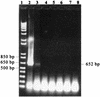
Infection with bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) occurs worldwide and causes serious economic losses due to the deaths of animals, abortions, decreased milk production, and loss of body weight. BHV-1 is frequently found in bovine semen and is transmitted through natural service and artificial insemination. The detection of BHV-1 in bovine semen is a long-standing problem in veterinary virology which is important in disease control schemes. In the present study, ordered deletions of the full-length BHV-1 glycoprotein open reading frame were used to identify an epitope recognized by a specific monoclonal antibody (MAb). A glycoprotein D fragment containing this epitope was then amplified using an in vitro protein amplification assay developed previously (J. Zhou, J. Lyaku, R. A. Fredrickson, and F. S. Kibenge, J. Virol. Methods 79:181-189, 1999), and the resulting peptide was detected by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with the specific MAb. This method detected 0.0395 50% tissue culture infective dose of BHV-1 in raw bovine semen, which was 1,000-fold more sensitive than traditional PCR. We therefore conclude that this in vitro protein amplification assay combined with ELISA has superior sensitivity for direct virus detection in clinical samples.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelmagid, O. Y., H. C. Minocha, J. K. Collins, and S. I. Chowdhury. 1995. Fine mapping of bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) glycoprotein D (gD) neutralizing epitopes by type-specific monoclonal antibodies and sequence comparison with BHV-5 gD. Virology 206:242-253. - PubMed
-
- Abdelmagid, O. Y., M. M. Mansour, O. Okwumabua, and L. van Drunen. 1998. Expression and cellular distribution of baculovirus-expressed bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) glycoprotein D (gD) sequences. Arch. Virol. 143:2173-2187. - PubMed
-
- Crowther, J. R. 2000. Validation of diagnostic tests, p. 311-313. In J. M. Walker (ed.), The ELISA guidebook. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J.
-
- Dubuisson, J., B. A. Israel, and G. J. Letchworth. 1992. Mechanisms of bovine herpesvirus type 1 neutralization by monoclonal antibodies to glycoproteins gI, gIII and gIV. J. Gen. Virol. 73:2031-2039. - PubMed
-
- Favre, D. 1992. Improved phenol-based method for the isolation of DNA fragments from low melting temperature agarose gels. BioTechniques 13:120-123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

