Detection of gyrA mutations in quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography
- PMID: 12409384
- PMCID: PMC139672
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4121-4125.2002
Detection of gyrA mutations in quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography
Abstract
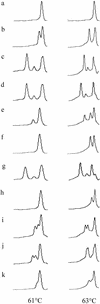
Denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) was evaluated as a rapid screening and identification method for DNA sequence variation detection in the quinolone resistance-determining region of gyrA from Salmonella serovars. A total of 203 isolates of Salmonella were screened using this method. DHPLC analysis of 14 isolates representing each type of novel or multiple mutations and the wild type were compared with LightCycler-based PCR-gyrA hybridization mutation assay (GAMA) and single-strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP) analyses. The 14 isolates gave seven different SSCP patterns, and LightCycler detected four different mutations. DHPLC detected 11 DNA sequence variants at eight different codons, including those detected by LightCycler or SSCP. One of these mutations was silent. Five isolates contained multiple mutations, and four of these could be distinguished from the composite sequence variants by their DHPLC profile. Seven novel mutations were identified at five different loci not previously described in quinolone-resistant salmonella. DHPLC analysis proved advantageous for the detection of novel and multiple mutations. DHPLC also provides a rapid, high-throughput alternative to LightCycler and SSCP for screening frequently occurring mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Andrews, J. M. 2001. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 48(Suppl. 1):5-16. - PubMed
-
- Giraud, E., A. Brisabois, J. L. Martel, and E. Chaslus-Dancla. 1999. Comparative studies of mutations in animal isolates and experimental in vitro- and in vivo-selected mutants of Salmonella spp. suggest a counterselection of highly fluoroquinolone-resistant strains in the field. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:2131-2137. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

