Long-term venous complications after full-size and segmental pediatric liver transplantation
- PMID: 12409673
- PMCID: PMC1422625
- DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200211000-00017
Long-term venous complications after full-size and segmental pediatric liver transplantation
Abstract
Objective: To assess the long-term incidence of venous complications, including portal vein and hepatic vein stenoses, in both whole cadaveric and reduced-size cadaveric and living related liver transplants in a pediatric population, and to assess the therapeutic modalities in the treatment of these lesions.
Summary background data: A shortage in appropriate-sized liver grafts for pediatric patients led to the use of segmental liver grafts, which became the predominant graft used in 325 of 600 (54%) transplants at the authors' institution. To assess the long-term impact of this strategy, the authors examined the incidence of late (>90 days) venous complications and the efficacy of all therapeutic interventions.
Methods: Six hundred pediatric liver transplants were performed in 325 patients, with reduced-size or split (RSS; n = 207), living related (LRD; n = 118), or full-size cadaveric grafts (FS; n = 275) from 1988 to 2000. All transplants identified with late portal vein or vena caval stenoses or thromboses from a cohort of 524 grafts with survival greater than 90 days were reviewed for demographics, symptoms, therapeutic intervention, recurrence, morbidity, and mortality.
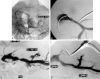
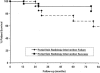
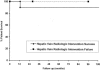
Results: Fifty lesions were identified in 49 patients (38 portal vein and 12 hepatic vein-cava stenoses). Sex distribution was similar between portal vein and hepatic vein to cava, as was the mean patient age. Portal vein stenoses occurred in 32 LRD, 3 RSS, and 3 FS, while hepatic vein-cava stenoses occurred in 2 LRD, 8 RSS, and 2 FS. In the 38 portal vein stenoses, 9 had prior perioperative portal vein and/or 5 hepatic artery thrombectomies. Portal vein stenoses were identified after bleeding (17/38), ascites (6/38), increased liver function tests (6/38), splenomegaly (5/38), or screening ultrasound (4/38). Portal vein stenosis was associated most often with cryopreserved vein for portal conduits. Excluding conduits, the incidence of late portal vein complications was reduced to 1%. Lesions became symptomatic at a mean of 50.8 +/- 184.2 months posttransplant. All patients underwent venous angioplasty with a 66% (25/38) success rate, while 7 of 25 required further angioplasty and stenting. In the 13 unsuccessful angioplasties, 8 required surgical shunts for complete portal vein thrombosis. Recurrence occurred in 9 patients: all were amenable to stenting. Nine patients (24%) eventually died of sepsis (4) and surgical deaths at shunt or retransplant (5). Hepatic vein-cava stenoses occurred after a mean of 37.2 +/- 35.2 months, presenting with ascites (n = 10), increased liver function tests (n = 2), and splenomegaly (n = 2). All patients were diagnosed by venogram and managed by balloon dilatation alone (n = 6) or stented (n = 4), with an 80% (10/12) success, with two late recurrences amenable to repeat angioplasty or stenting. Long-term survival was 80% at 1 year.
Conclusions: The use of segmental grafts without venous conduits is not associated with a significant rate of long-term venous complication. When late venous complications do occur, venous angioplasty and stenting are both a safe and effective management modality. If necessary, venous angioplasty may be repeated with the placement of a stent. When this is required, care must be taken to place the stent in a position where the metallic object will not interfere with future surgical manipulations should retransplantation be necessary.
Figures


References
-
- Whitington PF, Alonso EM, Piper JB. Pediatric liver transplantation. Semin Liver Dis 1994; 14: 303. - PubMed
-
- Whitington PF, Balisteri WF. Liver transplantation in pediatrics: indications, contraindications, and pre-transplant management. J Pediatr 1991; 118: 169. - PubMed
-
- Lilly JR, Hall RJ. Liver transplantation and Kasi operation in the first year of life: therapeutic dilemma in biliary atresia. J Pediatr 1987; 110: 561. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

