An active role for endogenous beta-1,3-glucanase genes in transgene-mediated co-suppression in tobacco
- PMID: 12411500
- PMCID: PMC131083
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf586
An active role for endogenous beta-1,3-glucanase genes in transgene-mediated co-suppression in tobacco
Abstract
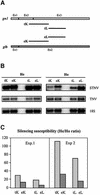
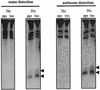
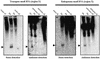
Post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) is characterized by the accumulation of short interfering RNAs that are proposed to mediate sequence-specific degradation of cognate and secondary target mRNAs. In plants, it is unclear to what extent endogenous genes contribute to this process. Here, we address the role of the endogenous target genes in transgene-mediated PTGS of beta-1,3-glucanases in tobacco. We found that mRNA sequences of the endogenous glucanase glb gene with varying degrees of homology to the Nicotiana plumbaginifolia gn1 transgene are targeted by the silencing machinery, although less efficiently than corresponding transgene regions. Importantly, we show that endogene-specific nucleotides in the glb sequence provide specificity to the silencing process. Consistent with this finding, small sense and antisense 21- to 23-nucleotide RNAs homologous to the endogenous glb gene were detected. Combined, these data demonstrate that a co-suppressed endogenous glucan ase gene is involved in signal amplification and selection of homologous targets, and show that endogenous genes can actively participate in PTGS in plants. The findings are introduced as a further sophistication of the post-transciptional silencing model.
Figures

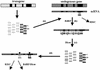
Similar articles
-
Posttranscriptional gene silencing of gn1 in tobacco triggers accumulation of truncated gn1-derived RNA species.RNA. 1999 Oct;5(10):1364-73. doi: 10.1017/s1355838299990799. RNA. 1999. PMID: 10573127 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional cosuppression of beta-1,3-glucanase genes does not affect accumulation of transgene nuclear mRNA.Plant Cell. 1995 Mar;7(3):347-58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.3.347. Plant Cell. 1995. PMID: 7734967 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of beta-1,3-glucanase genes in tobacco correlates with an increased abundance of RNA degradation intermediates.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Nov 15;26(22):5176-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.22.5176. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9801316 Free PMC article.
-
Co-suppression of beta-1,3-glucanase genes in Nicotiana tabacum.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;197:91-103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79145-1_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7493499 Review. No abstract available.
-
RNA as a target and an initiator of post-transcriptional gene silencing in transgenic plants.Plant Mol Biol. 1996 Oct;32(1-2):79-88. doi: 10.1007/BF00039378. Plant Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8980475 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Revealed the Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GSs) Deficiency on Expression of Storage Substances and the Potential Regulatory Mechanism of HMW-GSs.Foods. 2023 Jan 12;12(2):361. doi: 10.3390/foods12020361. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673453 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of RNA silencing in agroinfiltrated leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana and Nicotiana tabacum.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 Nov;59(4):647-61. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-0668-x. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16244913
-
An endogene-resembling transgene is resistant to DNA methylation and systemic silencing.RNA Biol. 2014;11(7):934-41. doi: 10.4161/rna.29623. Epub 2014 Jul 23. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 25180820 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-mediated endogene silencing in strawberry fruit: detection of primary and secondary siRNAs by deep sequencing.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 May;15(5):658-668. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12664. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27862816 Free PMC article.
-
RNA target sequences promote spreading of RNA silencing.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jan;131(1):245-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.009407. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12529532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andriessen M. (1997) Cis- and trans-acting elements in satellite tobacco necrosis virus RNA replication. PhD thesis, Ghent University, Belgium.
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy,A.A., Hammond,S.M. and Hannon,G.J. (2001) Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature, 409, 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Cogoni C. (2001) Homology-dependent gene silencing mechanisms in fungi. Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 55, 381–406. - PubMed
-
- Cogoni C. and Macino,G. (1999) Gene silencing in Neurospora crassa requires a protein homologous to RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature, 399, 166–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

