Excitation of rat colonic afferent fibres by 5-HT(3) receptors
- PMID: 12411529
- PMCID: PMC2290619
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.025452
Excitation of rat colonic afferent fibres by 5-HT(3) receptors
Abstract
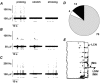
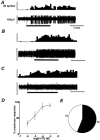
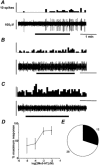
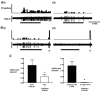
The gastrointestinal tract contains most of the body's 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and releases large amounts after meals or exposure to toxins. Increased 5-HT release occurs in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and their peak plasma 5-HT levels correlate with pain episodes. 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists reduce symptoms of IBS clinically, but their site of action is unclear and the potential for other therapeutic targets is unexplored. Here we investigated effects of 5-HT on sensory afferents from the colon and the expression of 5-HT(3) receptors on their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Distal colon, inferior mesenteric ganglion and the lumbar splanchnic nerve bundle (LSN) were placed in a specialized organ bath. Eighty-six single fibres were recorded from the LSN. Three classes of primary afferents were found: 70 high-threshold serosal afferents, four low-threshold muscular afferents and 12 mucosal afferents. Afferent cell bodies were retrogradely labelled from the distal colon to the lumbar DRG, where they were processed for 5-HT(3) receptor-like immunoreactivity. Fifty-six percent of colonic afferents responded to 5-HT (between 10(-6) and 10(-3) M) and 30 % responded to the selective 5-HT(3) agonist, 2-methyl-5-HT (between 10(-6) and 10(-2) M). Responses to 2-methyl-5-HT were blocked by the 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist alosetron (2 x 10(-7) M), whereas responses to 5-HT were only partly inhibited. Twenty-six percent of L1 DRG cell bodies retrogradely labelled from the colon displayed 5-HT(3) receptor-like immunoreactivity. We conclude that colonic sensory neurones expressing 5-HT(3) receptors also functionally express the receptors at their peripheral endings. Our data reveal actions of 5-HT on colonic afferent endings via both 5-HT(3) and non-5-HT(3) receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Andrews PLR, Davis CJ, Bingham S, Davidson HIM, Hawthorn J, Maskell L. The abdominal visceral innervation and the emetic reflex: pathways, pharmacology, and plasticity. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1990;68:325–345. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Janig W. Sympathetic and afferent somata projecting in hindlimb nerves and the anatomical organization of the lumbar sympathetic nervous system of the rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1988;275:460–468. - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR, Lynn PA, Blackshaw LA. Vagal and spinal mechanosensors in the rat stomach and colon have multiple receptive fields. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2001;280:R1371–1381. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Kunze WA, Furness JB, Bornstein JC. The terminals of myenteric intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the guinea-pig ileum are excited by 5-hydroxytryptamine acting at 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 receptors. Neuroscience. 2000;101:459–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

