Determination of cyclin D1 and CD20 mRNA levels by real-time quantitative RT-PCR from archival tissue sections of mantle cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin's lymphomas
- PMID: 12411587
- PMCID: PMC1907355
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60704-0
Determination of cyclin D1 and CD20 mRNA levels by real-time quantitative RT-PCR from archival tissue sections of mantle cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin's lymphomas
Abstract
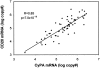
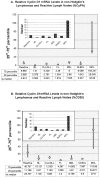
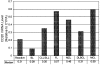
Cyclin D1 overexpression is a valuable marker for the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). We used a real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) method to quantify levels of cyclin D1, CD20, and cyclophilin A mRNA in manually microdissected, paraffin-embedded tissue sections using an ABI 7700 qRT-PCR system. The study group included 21 cases of MCL and 37 cases of other types of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cyclin D1 mRNA copy number was normalized to CD20 and cyclophilin A mRNA and evaluated statistically by analysis of variance. The relative cyclin D1 levels were similar whether normalized to CD20 or cyclophilin A, indicating that CD20 levels are stable and can be used as a B-cell-specific normalizer. Statistically significant differences were found in the median levels of cyclin D1 mRNA (expressed as % CD20 mRNA) among cases of MCL (87.6), small lymphocytic lymphoma (9.9), follicular lymphoma (2.4), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (5.9), marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (39.8), and Burkitt lymphoma (7.1) (P < 0.05). We conclude that qRT-PCR can be used to quantify cyclin D1 mRNA levels in archival tissue sections. Normalization of cyclin D1 to a B-cell-specific marker more accurately reflects overexpression by MCL than other methods that normalize using constitutively expressed mRNA species.
Figures
References
-
- Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO: Mantle cell lymphoma: an entity comes of age. Blood 1996, 87:4483-4494 - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Nathwani BN, Berger F, Piris MA, Isaacson PI, Harris NL, Muller-Hermelink HK: Mantle cell lymphoma. Jaffe ES Harris NL Stein H Vardiman J eds. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 2001:168-170 IARC Press Lyon, France
-
- Motokura T, Bloom T, Kim HG, Juppner H, Ruderman JV, Kronenberg HM, Arnold A: A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature 1991, 350:512-515 - PubMed
-
- Vasef MA, Medeiros LJ, Koo C, McCourty A, Brynes RK: Cyclin D1 immunohistochemical staining is useful in distinguishing mantle cell lymphoma from other low-grade B-cell neoplasms in bone marrow. Am J Clin Pathol 1997, 108:302-307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

