Constitutive retinal CD200 expression regulates resident microglia and activation state of inflammatory cells during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis
- PMID: 12414514
- PMCID: PMC1850781
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64444-6
Constitutive retinal CD200 expression regulates resident microglia and activation state of inflammatory cells during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis
Abstract
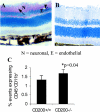
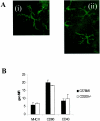
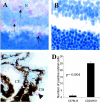
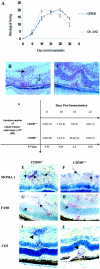
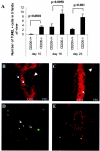
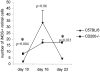
Recent evidence supports the notion that tissue OX2 (CD200) constitutively provides down-regulatory signals to myeloid-lineage cells via CD200-receptor (CD200R). Thus, mice lacking CD200 (CD200(-/-)) show increased susceptibility to and accelerated onset of tissue-specific autoimmunity. In the retina there is extensive expression of CD200 on neurons and retinal vascular endothelium. We show here that retinal microglia in CD200(-/-) mice display normal morphology, but unlike microglia from wild-type CD200(+/+) mice are present in increased numbers and most significantly, express inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2), a macrophage activation marker. Onset and severity of uveitogenic peptide (1-20) of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein-induced experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis is accelerated in CD200(-/-) mice and although tissue destruction appears no greater than seen in CD200(+/+) mice, there is continued increased ganglion and photoreceptor cell apoptosis. Myeloid cell infiltrate was increased in CD200(-/-) mice during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis, although NOS2 expression was not heightened. The results indicate that the CD200:CD200R axis regulates retinal microglial activation. In CD200(-/-) mice the release of suppression of tonic macrophage activation, supported by increased NOS2 expression in the CD200(-/-) steady state accelerates disease onset but without any demonstration of increased target organ/tissue destruction.
Figures
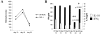
References
-
- Forrester JV, McMenamin PG: Immunopathogenic mechanisms in intraocular inflammation. Chem Immunol 1999, 73:159-185 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamenura F, Naito M: Differentiation, maturation and proliferation of macrophages in yolk sac: a light microscope, enzyme-cytochemical immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Leukoc Biol 1989, 45:87-96 - PubMed
-
- Yamada M, Naito M, Takahasi K: Kupffer cell proliferation and glucan induced granuloma formation in mice depleted of blood monocytes by strontium-89. J Leukoc Biol 1990, 47:195-205 - PubMed
-
- Rooijen N, Kors N, Vd Endn M, Dijkstra CD: Depletion and repopulation of macrophages in spleen and liver of rat after intravenous treatment with liposome encapsulated di-chloromethylene diphosphate. Cell Tissue Res 1990, 260:215-222 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

