Fas and fas ligand are up-regulated in pulmonary edema fluid and lung tissue of patients with acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 12414525
- PMCID: PMC1850801
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64455-0
Fas and fas ligand are up-regulated in pulmonary edema fluid and lung tissue of patients with acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
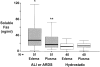
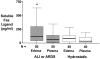
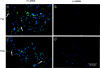
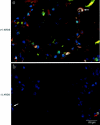
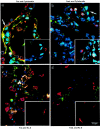
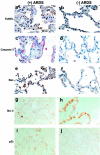
Apoptosis mediated by Fas/Fas ligand (FasL) interaction has been implicated in human disease processes, including pulmonary disorders. However, the role of the Fas/FasL system in acute lung injury (ALI) and in the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is poorly defined. Accordingly, we investigated both the soluble and cellular expression of the Fas/FasL system in patients with ALI or ARDS. The major findings are summarized as follows. First, the soluble expression of the Fas/FasL system was assessed in undiluted pulmonary edema fluid and simultaneous plasma. Pulmonary edema fluid obtained from patients with ALI or ARDS (n = 51) had significantly higher concentrations of both soluble Fas (27 ng/ml; median; P < 0.05) and soluble FasL (0.125 ng/ml; P < 0.05) compared to control patients with hydrostatic pulmonary edema (n = 40; soluble Fas, 12 ng/ml; soluble FasL, 0.080 ng/ml). In addition, the concentrations of both soluble Fas and soluble FasL were significantly higher in the pulmonary edema fluid of the patients with ALI or ARDS compared to simultaneous plasma samples (soluble Fas, 16 ng/ml; soluble FasL, 0.058 ng/ml; P < 0.05), indicating local release in the lung. Higher soluble Fas concentrations were associated with worse clinical outcomes. Second, cellular expression of the Fas/FasL system was assessed by semiquantitative immunofluorescence microscopy in lung tissue obtained at autopsy from a different set of patients. Both Fas and FasL were immunolocalized to a greater extent in the patients who died with ALI or ARDS (n = 10) than in the patients who died without pulmonary disease (n = 10). Both proteins were co-expressed by epithelial cells that lined the alveolar walls, as well as by inflammatory cells and sloughed epithelial cells that were located in the air spaces. Semiquantitative immunohistochemistry showed that markers of apoptosis (terminal dUTP nick-end labeling, caspase-3, Bax, and p53) were more prevalent in alveolar wall cells from the patients who died with ALI or ARDS compared to the patients who died without pulmonary disease. These findings indicate that alveolar epithelial injury in humans with ALI or ARDS is in part associated with local up-regulation of the Fas/FasL system and activation of the apoptotic cascade in the epithelial cells that line the alveolar air spaces.
Figures

References
-
- Matthay MA, Wiener-Kronish JP: Intact epithelial barrier function is critical for the resolution of alveolar edema in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis 1990, 142:1250-1257 - PubMed
-
- Bachofen M, Weibel ER: Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis 1977, 116:589-615 - PubMed
-
- Hamann KJ, Dorscheid DR, Ko FD, Conforti AE, Sperling AI, Rabe KF, White SR: Expression of Fas (CD95) and FasL (CD95L) in human airway epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1998, 19:537-542 - PubMed
-
- Matute-Bello G, Liles WC, Steinberg KP, Kiener PA, Kiener S, Mongovin S, Chi EY, Jonas M, Martin TR: Soluble Fas-ligand induces epithelial cell apoptosis in humans with acute lung injury (ARDS). J Immunol 1999, 163:2217-2225 - PubMed
-
- Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y, Nagata S: The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 1991, 66:233-243 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

