Identification of genes involved in resistance to interferon-alpha in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 12414529
- PMCID: PMC1850769
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64459-8
Identification of genes involved in resistance to interferon-alpha in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
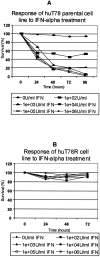
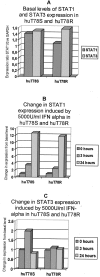
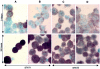
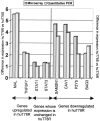
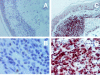
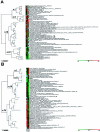
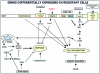
Interferon-alpha therapy has been shown to be active in the treatment of mycosis fungoides although the individual response to this therapy is unpredictable and dependent on essentially unknown factors. In an effort to better understand the molecular mechanisms of interferon-alpha resistance we have developed an interferon-alpha resistant variant from a sensitive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line. We have performed expression analysis to detect genes differentially expressed between both variants using a cDNA microarray including 6386 cancer-implicated genes. The experiments showed that resistance to interferon-alpha is consistently associated with changes in the expression of a set of 39 genes, involved in signal transduction, apoptosis, transcription regulation, and cell growth. Additional studies performed confirm that STAT1 and STAT3 expression and interferon-alpha induction and activation are not altered between both variants. The gene MAL, highly overexpressed by resistant cells, was also found to be expressed by tumoral cells in a series of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients treated with interferon-alpha and/or photochemotherapy. MAL expression was associated with longer time to complete remission. Time-course experiments of the sensitive and resistant cells showed a differential expression of a subset of genes involved in interferon-response (1 to 4 hours), cell growth and apoptosis (24 to 48 hours.), and signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interferon-alpha resistance in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line is associated with lack of STAT1 expression.Blood. 1998 Jan 15;91(2):570-6. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9427711
-
Transcriptional response of T cells to IFN-alpha: changes induced in IFN-alpha-sensitive and resistant cutaneous T cell lymphoma.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004 Mar;24(3):185-95. doi: 10.1089/107999004322917034. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004. PMID: 15035852
-
Interferon-gamma inhibits interferon-alpha signalling in hepatic cells: evidence for the involvement of STAT1 induction and hyperexpression of STAT1 in chronic hepatitis C.Biochem J. 2004 Apr 1;379(Pt 1):199-208. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031495. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14690454 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of alpha-interferon with chemotherapeutic agents: effects on cytotoxic drug metabolism and multiple drug resistance.Med Oncol. 1995 Mar;12(1):9-14. doi: 10.1007/BF01571403. Med Oncol. 1995. PMID: 8542251 Review. No abstract available.
-
Alpha interferon: new associations in haematology/oncology. The Montpellier experience.Med Oncol. 1995 Mar;12(1):59-61. doi: 10.1007/BF01571410. Med Oncol. 1995. PMID: 8542249 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the immune system in the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphomas.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 12;12:1071171. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1071171. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36713518 Free PMC article.
-
MAL gene overexpression as a marker of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma stem-like cells that predicts chemoresistance and poor prognosis.BMC Cancer. 2017 May 25;17(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3334-1. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28545541 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling integrated into network modelling reveals heterogeneity in the mechanisms of BRCA1 tumorigenesis.Br J Cancer. 2009 Oct 20;101(8):1469-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605275. Br J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19826428 Free PMC article.
-
GEPAS: A web-based resource for microarray gene expression data analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3461-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg591. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12824345 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Profiling of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Reveals Underlying Heterogeneity Associated with Disease Progression.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 15;25(10):2996-3005. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3309. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30718356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD: How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 1998, 67:227-264 - PubMed
-
- Platanias LC: Interferons: laboratory to clinic investigations. Curr Opin Oncol 1995, 7:560-565 - PubMed
-
- Ihle JN, Witthuhn BA, Quelle FW, Yamamoto K, Thierfelder WE, Kreider B, Silvennoinen O: Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem Sci 1994, 19:222-227 - PubMed
-
- Darnell JR JE, Kerr IM, Stark GR: Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264:1415-1421 - PubMed
-
- Sangfelt O, Erickson S, Castro J, Heiden T, Einhorn S, Grander D: Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell growth are independent responses to interferon-alpha in hematopoietic cell lines. Cell Growth Differ 1997, 8:343-352 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

