Generation of C5a by phagocytic cells
- PMID: 12414531
- PMCID: PMC1850785
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64461-6
Generation of C5a by phagocytic cells
Abstract
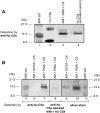
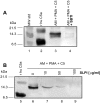
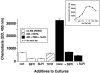
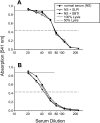
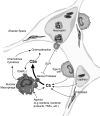
The complement activation product, C5a, is a powerful phlogistic factor. Using antibodies to detect human or rat C5a, incubation at pH 7.4 of human blood neutrophils or rat alveolar macrophages (AMs) with C5 in the presence of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) led to generation of C5a. Rat AMs activated with lipopolysaccharide also generated C5a from C5. With activated neutrophils, extensive cleavage of C5 occurred, whereas activated macrophages had much more selective proteolytic activity for C5. Peripheral blood human or rat mononuclear cells and rat alveolar epithelial cells when stimulated with phorbol ester all failed to demonstrate an ability to cleave C5, suggesting a specificity of C5 cleavage by phagocytic cells. With rat AMs, C5a generation was time-dependent and was blocked if AMs were pretreated with inhibitors of transcription or protein synthesis (actinomycin D or cycloheximide). Similar treatment of activated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes only partially reduced C5a generation after addition of C5. C5a generated by activated AMs was biologically (chemotactically) active. This generation was sensitive to serine protease inhibitors but not to other classes of inhibitors. These data indicate that phagocytic cells, especially lung macrophages, can generate C5a from C5. In the context of the lung, this may represent an important C5a-generating pathway that is independent of the plasma complement system.
Figures
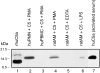
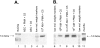
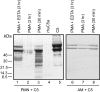
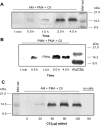
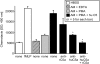

References
-
- Ishii Y, Kobayashi J, Kitamura S: Chemotactic factor generation and cell accumulation in acute lung injury induced by endotracheal acid instillation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1989, 37:65-70 - PubMed
-
- Sibille Y, Reynolds HY: Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Med 1990, 141:471-501 - PubMed
-
- Solomkin JS, Cotta LA, Satoh PS, Hurst JM, Nelson RD: Complement activation and clearance in acute illness and injury: evidence for C5a as a cell-directed mediator of the adult respiratory distress syndrome in man. Surgery 1984, 97:668-678 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

