Induction of intestinal inflammation in mouse by activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2
- PMID: 12414536
- PMCID: PMC1850779
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64466-5
Induction of intestinal inflammation in mouse by activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2
Abstract
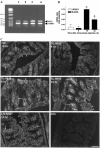
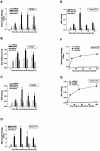
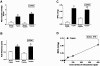
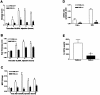
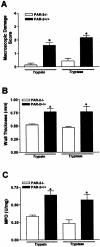
Proteinase-activated receptor (PAR)-2, a G-protein-coupled receptor for trypsin and mast cell tryptase, is highly expressed in the intestine. Luminal trypsin and tryptase are elevated in the colon of inflammatory bowel disease patients. We hypothesized that luminal proteinases activate PAR-2 and induce colonic inflammation. Mice received intracolonically PAR-2 agonists (trypsin, tryptase, and a selective PAR-2-activating peptide) or control drugs (boiled enzymes, inactive peptide) and inflammatory parameters were followed at various times after this treatment. Colonic administration of PAR-2 agonists up-regulated PAR-2 expression and induced an inflammatory reaction characterized by granulocyte infiltration, increased wall thickness, tissue damage, and elevated T-helper cell type 1 cytokine. The inflammation was maximal between 4 and 6 hours and was resolved 48 hours after the intracolonic administration. PAR-2 activation also increased paracellular permeability of the colon and induced bacterial trans-location into peritoneal organs. These proinflammatory and pathophysiological changes observed in wild-type mice were not detected in PAR-2-deficient mice. Luminal proteinases activate PAR-2 in the mouse colon to induce inflammation and disrupt the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Because trypsin and tryptase are found at high levels in the colon lumen of patients with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, our data may bear directly on the pathophysiology of human inflammatory bowel diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Brass LF, Molino M: Protease-activated G protein-coupled receptors on human platelets and endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 1997, 78:234-241 - PubMed
-
- Vergnolle N: Review article: proteinase-activated receptors-novel signals for gastrointestinal pathophysiology. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000, 14:257-266 - PubMed
-
- Vergnolle N, Wallace JL, Bunnett NW, Hollenberg MD: Protease-activated receptors in inflammation, neuronal signaling and pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2001, 22:146-152 - PubMed
-
- Vu T, Hung D, Wheaton V, Coughlin S: Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell 1991, 64:1057-1068 - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi-Matsui M, Zheng YW, Sulciner DJ, Weiss EJ, Ludeman MJ, Coughlin SR: PAR3 is a cofactor for PAR4 activation by thrombin. Nature 2000, 404:609-613 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

