Strand pairing by Rad54 and Rad51 is enhanced by chromatin
- PMID: 12414729
- PMCID: PMC187467
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1032102
Strand pairing by Rad54 and Rad51 is enhanced by chromatin
Abstract
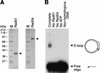
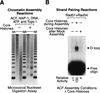
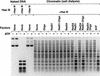
We investigated the role of chromatin in the catalysis of homologous strand pairing by Rad54 and Rad51. Rad54 is related to the ATPase subunits of chromatin-remodeling factors, whereas Rad51 is related to bacterial RecA. In the absence of superhelical tension, we found that the efficiency of strand pairing with chromatin is >100-fold higher than that with naked DNA. In addition, we observed that Rad54 and Rad51 function cooperatively in the ATP-dependent remodeling of chromatin. These findings indicate that Rad54 and Rad51 have evolved to function with chromatin, the natural substrate, rather than with naked DNA.
Figures


References
-
- Baumann P, West SC. Heteroduplex formation by human Rad51 protein: Effects of DNA end-structure, hRP-A and hRad52. J Mol Biol. 1999;291:363–374. - PubMed
-
- Becker PB, Hörz W. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:247–273. - PubMed
-
- Benson FE, Baumann P, West SC. Synergistic actions of Rad51 and Rad52 in recombination and DNA repair. Nature. 1998;391:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Logie C, Bonte E, Becker PB, Wade PA, Wolffe AP, Wu C, Imbalzano AN, Peterson CL. Functional delineation of three groups of the ATP-dependent family of chromatin remodeling enzymes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18864–18870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
