Differential regulation of the inhibitor of apoptosis ch-IAP1 by v-rel and the proto-oncogene c-rel
- PMID: 12414938
- PMCID: PMC136878
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.11960-11970.2002
Differential regulation of the inhibitor of apoptosis ch-IAP1 by v-rel and the proto-oncogene c-rel
Abstract
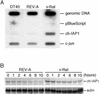
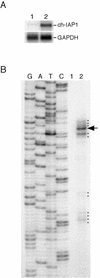
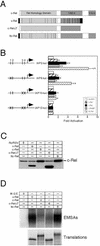
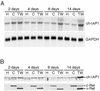
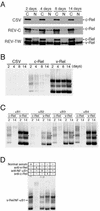
The v-rel oncogene encoded by reticuloendotheliosis virus is the acutely transforming member of the Rel/NF-kappaB family of transcription factors. v-Rel is a truncated and mutated form of c-Rel and transforms cells by inducing the aberrant expression of genes regulated by Rel/NF-kappaB proteins. The expression of ch-IAP1, a member of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis family, is highly elevated in cells expressing v-Rel and contributes to the immortalization of cells transformed by this oncoprotein. In this study we demonstrate that the elevated expression of ch-IAP1 in v-Rel-expressing cells is due to an increased rate of transcription. The ch-IAP1 promoter was isolated, and four Rel/NF-kappaB binding sites were identified upstream of the transcription start site. Two kappaB sites proximal to the transcription start site were required for v-Rel to activate the ch-IAP1 promoter. While c-Rel also utilized these sites, a third more-distal kappaB site was required for its full activation of the ch-IAP1 promoter. Differences in the transactivation domains of v-Rel and c-Rel are responsible for their different abilities to utilize these sites and account for their differential activation of the ch-IAP1 promoter. Although c-Rel was a more potent activator of the ch-IAP1 promoter than v-Rel in transient reporter assays, cells stably overexpressing c-Rel failed to maintain high levels of ch-IAP1 expression. The reduction of ch-IAP1 expression in these cells correlated with the efficient regulation of c-Rel by IkappaBalpha. The ability of v-Rel to escape IkappaBalpha regulation allows for the gradual and sustained elevation of ch-IAP1 expression directly contributing to the transforming properties of v-Rel.
Figures


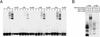
Similar articles
-
ch-IAP1, a member of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein family, is a mediator of the antiapoptotic activity of the v-Rel oncoprotein.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):7328-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.7328. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372964 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of v-Rel oncogene-induced inhibitor of apoptosis by differential display.Methods. 1998 Dec;16(4):373-85. doi: 10.1006/meth.1998.0692. Methods. 1998. PMID: 10049645
-
Avian I kappa B alpha is transcriptionally induced by c-Rel and v-Rel with different kinetics.J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5383-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.9.5383-5390.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7636983 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of the chicken c-rel promoter by vRel in chicken embryo fibroblasts is not mediated through a consensus NF-kappa B binding site.Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2203-10. Oncogene. 1991. PMID: 1766669
-
c-Rel and its many roles in cancer: an old story with new twists.Br J Cancer. 2016 Jan 12;114(1):1-6. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.410. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26757421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of telomerase activation by v-Rel and its contribution to transformation.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(1):281-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.281-295.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16352553 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of B-cell linker (BLNK) and B-cell adaptor for phosphoinositide 3-kinase (BCAP) is important for lymphocyte transformation by rel proteins.Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 1;68(3):808-14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3169. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18245482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashkenazi, A., and V. M. Dixit. 1998. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305-1308. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T. W., B. P. Giroir, and E. H. Humphries. 1985. Cell lines derived from avian lymphomas exhibit two distinct phenotypes. Virology 144:139-151. - PubMed
-
- Bose, H. R., Jr. 1992. The Rel family: models for transcriptional regulation and oncogenic transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1114:1-17. - PubMed
-
- Davis, N., S. Ghosh, D. L. Simmons, P. Tempst, H. C. Liou, D. Baltimore, and H. R. Bose, Jr. 1991. Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the Rel family of transcription factors. Science 253:1268-1271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

