The hydrophilic amino-terminal arm of reovirus core shell protein lambda1 is dispensable for particle assembly
- PMID: 12414960
- PMCID: PMC136864
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.12211-12222.2002
The hydrophilic amino-terminal arm of reovirus core shell protein lambda1 is dispensable for particle assembly
Abstract
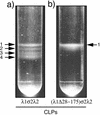
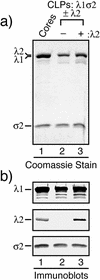
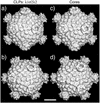
The reovirus core particle is a molecular machine that mediates synthesis, capping, and export of the viral plus strand RNA transcripts. Its assembly and structure-function relationships remain to be well understood. Following the lead of previous studies with other Reoviridae family members, most notably orbiviruses and rotaviruses, we used recombinant baculoviruses to coexpress reovirus core proteins lambda1, lambda2, and sigma2 in insect cells. The resulting core-like particles (CLPs) were purified and characterized. They were found to be similar to cores with regard to their sizes, morphologies, and protein compositions. Like cores, they could also be coated in vitro with the two major outer-capsid proteins, micro 1 and sigma3, to produce virion-like particles. Coexpression of core shell protein lambda1 and core nodule protein sigma2 was sufficient to yield CLPs that could withstand purification, whereas expression of lambda1 alone was not, indicating a required role for sigma2 as a previous study also suggested. In addition, CLPs that lacked lambda2 (formed from lambda1 and sigma2 only) could not be coated with micro 1 and sigma3, indicating a required role for lambda2 in the assembly of these outer-capsid proteins into particles. To extend the use of this system for understanding the core and its assembly, we addressed the hypothesis that the hydrophilic amino-terminal region of lambda1, which adopts an extended arm-like conformation around each threefold axis in the reovirus core crystal structure, plays an important role in assembling the core shell. Using a series of lambda1 deletion mutants, we showed that the amino-terminal 230 residues of lambda1, including its zinc finger, are dispensable for CLP assembly. Residues in the 231-to-259 region of lambda1, however, were required. The core crystal structure suggests that residues in the 231-to-259 region are necessary because they affect the interaction of lambda1 with the threefold and/or fivefold copies of sigma2. An effective system for studies of reovirus core structure, assembly, and functions is hereby established.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Reovirus Core Proteins λ1 and σ2 Promote Stability of Disassembly Intermediates and Influence Early Replication Events.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e00491-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00491-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581098 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of activities for mRNA synthesis accompanies loss of lambda2 spikes from reovirus cores: an effect of lambda2 on lambda1 shell structure.Virology. 2002 Apr 25;296(1):24-38. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1258. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12036315
-
In vitro recoating of reovirus cores with baculovirus-expressed outer-capsid proteins mu1 and sigma3.J Virol. 1999 May;73(5):3941-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.5.3941-3950.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10196289 Free PMC article.
-
Attachment and cell entry of mammalian orthoreovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;309:1-38. doi: 10.1007/3-540-30773-7_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16909895 Review.
-
Nonstructural proteins involved in genome packaging and replication of rotaviruses and other members of the Reoviridae.Virus Res. 2004 Apr;101(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2003.12.006. Virus Res. 2004. PMID: 15010217 Review.
Cited by
-
Localization of mammalian orthoreovirus proteins to cytoplasmic factory-like structures via nonoverlapping regions of microNS.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(2):867-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01571-09. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19889754 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Mismatches Caused by Reassortment Influence Functions of the Reovirus Capsid.J Virol. 2018 Sep 26;92(20):e00858-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00858-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30068646 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of S9 segment of grass carp reovirus Anhui strain.Virusdisease. 2017 Mar;28(1):26-32. doi: 10.1007/s13337-016-0357-1. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Virusdisease. 2017. PMID: 28466052 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus nonstructural protein mu NS recruits viral core surface proteins and entering core particles to factory-like inclusions.J Virol. 2004 Feb;78(4):1882-92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.4.1882-1892.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14747553 Free PMC article.
-
The amino-terminal region of major capsid protein P3 is essential for self-assembly of single-shelled core-like particles of Rice dwarf virus.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(6):3145-8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.6.3145-3148.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14990734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker, T. S., and R. H. Cheng. 1996. A model-based approach for determining orientations of biological macromolecules imaged by cryo-electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 116:120-130. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, A. K., and M. A. Grece. 1971. An identical 3′-terminal sequence in the ten reovirus genome RNA segments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 45:1518-1525. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, A. K., R. Ward, and A. J. Shatkin. 1971. Cytosine at the 3′-termini of reovirus genome and in vitro mRNA. Nat. New Biol. 232:114-115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

