Langerhans cells renew in the skin throughout life under steady-state conditions
- PMID: 12415265
- PMCID: PMC4727838
- DOI: 10.1038/ni852
Langerhans cells renew in the skin throughout life under steady-state conditions
Erratum in
- Nat Immunol 2003 Jan;4(1):92
Abstract
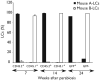
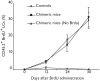
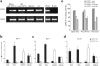
Langerhans cells (LCs) are bone marrow (BM)-derived epidermal dendritic cells (DCs) that represent a critical immunologic barrier to the external environment, but little is known about their life cycle. Here, we show that in lethally irradiated mice that had received BM transplants, LCs of host origin remained for at least 18 months, whereas DCs in other organs were almost completely replaced by donor cells within 2 months. In parabiotic mice with separate organs, but a shared blood circulation, there was no mixing of LCs. However, in skin exposed to ultraviolet light, LCs rapidly disappeared and were replaced by circulating LC precursors within 2 weeks. The recruitment of new LCs was dependent on their expression of the CCR2 chemokine receptor and on the secretion of CCR2-binding chemokines by inflamed skin. These data indicate that under steady-state conditions, LCs are maintained locally, but inflammatory changes in the skin result in their replacement by blood-borne LC progenitors.
Figures

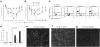

Comment in
-
Langerhans cells: immigrants or residents?Nat Immunol. 2002 Dec;3(12):1125-6. doi: 10.1038/ni1202-1125. Nat Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12447368 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schuler G, et al. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells as a model to study tissue dendritic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;329:243–249. - PubMed
-
- Stingl G, Tamaki K, Katz SI. Origin and function of epidermal Langerhans cells. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:149–174. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
-
- Jakob T, Ring J, Udey MC. Multistep navigation of Langerhans/dendritic cells in and out of the skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:688–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

