Proteomic characterization of the small subunit of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast ribosome: identification of a novel S1 domain-containing protein and unusually large orthologs of bacterial S2, S3, and S5
- PMID: 12417713
- PMCID: PMC152739
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.004341
Proteomic characterization of the small subunit of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast ribosome: identification of a novel S1 domain-containing protein and unusually large orthologs of bacterial S2, S3, and S5
Abstract
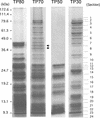
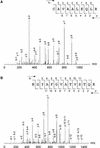
To understand how chloroplast mRNAs are translated into functional proteins, a detailed understanding of all of the components of chloroplast translation is needed. To this end, we performed a proteomic analysis of the plastid ribosomal proteins in the small subunit of the chloroplast ribosome from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Twenty proteins were identified, including orthologs of Escherichia coli S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S9, S10, S12, S13, S14, S15, S16, S17, S18, S19, S20, and S21 and a homolog of spinach plastid-specific ribosomal protein-3 (PSRP-3). In addition, a novel S1 domain-containing protein, PSRP-7, was identified. Among the identified proteins, S2 (57 kD), S3 (76 kD), and S5 (84 kD) are prominently larger than their E. coli or spinach counterparts, containing N-terminal extensions (S2 and S5) or insertion sequence (S3). Structural predictions based on the crystal structure of the bacterial 30S subunit suggest that the additional domains of S2, S3, and S5 are located adjacent to each other on the solvent side near the binding site of the S1 protein. These additional domains may interact with the S1 protein and PSRP-7 to function in aspects of mRNA recognition and translation initiation that are unique to the Chlamydomonas chloroplast.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic characterization of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast ribosome. Identification of proteins unique to th e70 S ribosome.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):33774-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301934200. Epub 2003 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12826678
-
The small subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome. Identification of the full complement of ribosomal proteins present.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):19363-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100727200. Epub 2001 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11279123
-
Efficient reconstitution of functional Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits from a complete set of recombinant small subunit ribosomal proteins.RNA. 1999 Jun;5(6):832-43. doi: 10.1017/s1355838299990714. RNA. 1999. PMID: 10376881 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at the crossroads of genomics.Eukaryot Cell. 2003 Dec;2(6):1137-50. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.6.1137-1150.2003. Eukaryot Cell. 2003. PMID: 14665449 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A comparative inventory of metal transporters in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and the red alga Cyanidioschizon merolae.Plant Physiol. 2005 Feb;137(2):428-46. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.054189. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15710683 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expression and RNA binding properties of the chloroplast ribosomal protein S1 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 Oct;53(3):371-82. doi: 10.1023/b:plan.0000006941.56233.42. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14750525
-
Cadmium response and redoxin targets in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a proteomic approach.Photosynth Res. 2006 Sep;89(2-3):201-11. doi: 10.1007/s11120-006-9108-2. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Photosynth Res. 2006. PMID: 17103236
-
Pyrenoid functions revealed by proteomics in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 26;13(2):e0185039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185039. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29481573 Free PMC article.
-
The versatile interactome of chloroplast ribosomes revealed by affinity purification mass spectrometry.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 11;49(1):400-415. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1192. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33330923 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 27;14(11):1634. doi: 10.3390/plants14111634. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold, R.J., and Reilly, J.P. (1999). Observation of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins and their posttranslational modifications by mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 269, 105–112. - PubMed
-
- Barkan, A., and Goldschmidt-Clermont, M. (2000). Participation of nuclear genes in chloroplast gene expression. Biochimie 82, 559–572. - PubMed
-
- Bourque, D.P., Boynton, J.E., and Gillham, N.W. (1971). Studies on the structure and cellular location of various ribosome and ribosomal RNA species in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Cell Sci. 8, 153–183. - PubMed
-
- Bruce, B.D. (2000). Chloroplast transit peptides: Structure, function and evolution. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 440–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

