Retroviral delivery of small interfering RNA into primary cells
- PMID: 12417750
- PMCID: PMC137524
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.242594499
Retroviral delivery of small interfering RNA into primary cells
Abstract
RNA interference is an evolutionarily conserved process in which recognition of double-stranded RNA ultimately leads to posttranscriptional suppression of gene expression. This suppression is mediated by short (21- to 22-nt) small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which induce degradation of mRNA based on complementary base pairing. The silencing of gene expression by siRNAs is emerging rapidly as a powerful method for genetic analysis. Recently, several groups have reported systems designed to express siRNAs in mammalian cells through transfection of either oligonucleotides or plasmids encoding siRNAs. Because these systems rely on transfection for delivery, the cell types available for study are restricted generally to transformed cell lines. Here, we describe a retroviral system for delivery of siRNA into cells. The use of retroviral vectors can greatly expand the types of cells available for RNA interference analysis. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this retroviral system allows for stable inactivation of genes in primary cells.
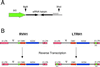
Figures



References
-
- Williams B. R. (1999) Oncogene 18, 6112-6120. - PubMed
-
- Sharp P. A. (2001) Genes Dev. 15, 485-490. - PubMed
-
- Fire A., Xu, S., Montgomery, M. K., Kostas, S. A., Driver, S. E. & Mello, C. C. (1998) Nature 391, 806-811. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir S. M., Harborth, J., Lendeckel, W., Yalcin, A., Weber, K. & Tuschl, T. (2001) Nature 411, 494-498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

