Cytoskeletal-assisted dynamics of the mitochondrial reticulum in living cells
- PMID: 12417764
- PMCID: PMC137494
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.232346999
Cytoskeletal-assisted dynamics of the mitochondrial reticulum in living cells
Abstract
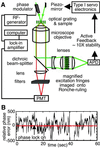
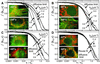
Subcellular organelle dynamics are strongly influenced by interactions with cytoskeletal filaments and their associated motor proteins, and lead to complex multiexponential relaxations that occur over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Here we report spatio-temporal measurements of the fluctuations of the mitochondrial reticulum in osteosarcoma cells by using Fourier imaging correlation spectroscopy, over time and distance scales of 10(-2) to 10(3) s and 0.5-2.5 microm. We show that the method allows a more complete description of mitochondrial dynamics, through the time- and length-scale-dependent collective diffusion coefficient D(k,tau), than available by other means. Addition of either nocodazole to disrupt microtubules or cytochalasin D to disassemble microfilaments simplifies the intermediate scattering function. When both drugs are used, the reticulum morphology of mitochondria is retained even though the cytoskeletal elements have been de-polymerized. The dynamics of the organelle are then primarily diffusive and can be modeled as a collection of friction points interconnected by elastic springs. This study quantitatively characterizes organelle dynamics in terms of collective cytoskeletal interactions in living cells.
Figures
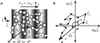
Similar articles
-
Cell elasticity with altered cytoskeletal architectures across multiple cell types.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016 Aug;61:197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.01.022. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016. PMID: 26874250
-
Reorganization of keratin intermediate filaments by the drug-induced disruption of microfilaments in cultured human keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Nov;87(5):565-9. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12455792. J Invest Dermatol. 1986. PMID: 2430025
-
Gap junctions assemble in the presence of cytoskeletal inhibitors, but enhanced assembly requires microtubules.Exp Cell Res. 2002 Apr 15;275(1):67-80. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5480. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 11925106
-
The relationship between mitochondrial shape and function and the cytoskeleton.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May-Jun;1757(5-6):692-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.04.013. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16729962 Review.
-
Design Principles of Length Control of Cytoskeletal Structures.Annu Rev Biophys. 2016 Jul 5;45:85-116. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070915-094206. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Annu Rev Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27145876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Actin polymerization driven mitochondrial transport in mating S. cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 12;107(2):721-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908338107. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080741 Free PMC article.
-
From Cell Architecture to Mitochondrial Signaling: Role of Intermediate Filaments in Health, Aging, and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 27;26(3):1100. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031100. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Mitochondria and Cytoskeleton in Cardiac Cells.Cells. 2020 Jan 16;9(1):222. doi: 10.3390/cells9010222. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31963121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RhoA and DIAPH1 mediate adrenocorticotropin-stimulated cortisol biosynthesis by regulating mitochondrial trafficking.Endocrinology. 2010 Sep;151(9):4313-23. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0044. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20591975 Free PMC article.
-
Anomalous Dynamics in Macromolecular Liquids.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 22;14(5):856. doi: 10.3390/polym14050856. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267678 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

