Segmental polymorphisms in the proterminal regions of a subset of human chromosomes
- PMID: 12421753
- PMCID: PMC187550
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.322802
Segmental polymorphisms in the proterminal regions of a subset of human chromosomes
Abstract
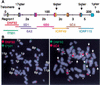
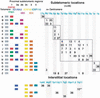
The subtelomeric domains of chromosomes are probably the most rapidly evolving structures of the human genome. The highly variable distribution of large duplicated subtelomeric segments has indicated that frequent exchanges between nonhomologous chromosomes may have been taking place during recent genome evolution. We have studied the extent and variability of such duplications using in situ hybridization techniques and a set of well-defined subtelomeric cosmid probes that identify discrete regions within the subtelomeric domain. In addition to reciprocal translocation and illegitimate recombination events that could explain the observed mosaic pattern of subtelomeric regions, it is likely that homology-based recombination mechanisms have also contributed to the spread of distal subtelomeric sequences among particular groups of nonhomologous chromosome arms. The frequency and distribution of large-scale subtelomeric polymorphisms may have direct implications for the design of chromosome-specific probes that are aimed at the identification of cryptic subtelomeric deletions. Furthermore, our results indicate that the relevance of some of the telomere closures proposed within the present Human Genome Sequence draft are restricted to specific allelic variants of unknown frequencies.
Figures
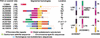
Similar articles
-
Human subtelomeres are hot spots of interchromosomal recombination and segmental duplication.Nature. 2005 Sep 1;437(7055):94-100. doi: 10.1038/nature04029. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16136133 Free PMC article.
-
The evolutionary origin of human subtelomeric homologies--or where the ends begin.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Apr;70(4):972-84. doi: 10.1086/339768. Epub 2002 Mar 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11875757 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of segmental duplication in the human genome.Mol Biol Evol. 2005 Jan;22(1):135-41. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh262. Epub 2004 Sep 15. Mol Biol Evol. 2005. PMID: 15371527
-
[Segment duplications in the human genome].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2003 Mar-Apr;37(2):212-20. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2003. PMID: 12723468 Review. Russian.
-
Human subtelomere structure and variation.Chromosome Res. 2005;13(5):505-15. doi: 10.1007/s10577-005-0998-1. Chromosome Res. 2005. PMID: 16132815 Review.
Cited by
-
The heterochromatic chromosome caps in great apes impact telomere metabolism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 May;41(9):4792-801. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt169. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23519615 Free PMC article.
-
The very long telomeres in Sorex granarius (Soricidae, Eulipothyphla) contain ribosomal DNA.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(7):881-90. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1170-x. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17899406
-
Human subtelomeric duplicon structure and organization.Genome Biol. 2007;8(7):R151. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-7-r151. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17663781 Free PMC article.
-
Toward closing rice telomere gaps: mapping and sequence characterization of rice subtelomere regions.Theor Appl Genet. 2005 Aug;111(3):467-78. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-2034-4. Epub 2005 Jun 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2005. PMID: 15965650
-
Human subtelomeres are hot spots of interchromosomal recombination and segmental duplication.Nature. 2005 Sep 1;437(7055):94-100. doi: 10.1038/nature04029. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16136133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH. Telomere states and cell fates. Nature. 2000;408:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Brown WR, MacKinnon PJ, Villasante A, Spurr N, Buckle VJ, Dobson MJ. Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA. Cell. 1990;63:119–132. - PubMed
-
- Ciccodicola A, D'Esposito M, Esposito T, Gianfrancesco F, Migliaccio C, Miano MG, Matarazzo MR, Vacca M, Franze A, Cuccurese M, et al. Differentially regulated and evolved genes in the fully sequenced Xq/Yq pseudoautosomal region. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:395–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
