Identification of phosphorylated residues that affect the activity of the mitotic kinase Aurora-A
- PMID: 12422018
- PMCID: PMC137735
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.202606599
Identification of phosphorylated residues that affect the activity of the mitotic kinase Aurora-A
Abstract
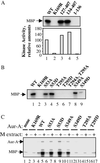
The activity of the kinase Aurora-A (Aur-A) peaks during mitosis and depends on phosphorylation by one or more unknown kinases. Mitotic phosphorylation sites were mapped by mass spec sequencing of recombinant Aur-A protein that had been activated by incubation in extracts of metaphase-arrested Xenopus eggs. Three sites were identified: serine 53 (Ser-53), threonine 295 (Thr-295), and serine 349 (Ser-349), which are equivalent to Ser-51, Thr-288, and Ser-342, respectively, in human Aur-A. To ask how phosphorylation of these residues might affect kinase activity, each was mutated to either alanine or aspartic acid, and the recombinant proteins were then tested for their ability to be activated by M phase extract. Mutation of Thr-295, which resides in the activation loop of the kinase, to either alanine or aspartic acid abolished activity. The S349A mutant had slightly reduced activity, indicating that phosphorylation is not required for activity. The S349D mutation completely blocked activation, suggesting that Ser-349 is important for either the structure or regulation of Aur-A. Finally, like human Aur-A, overexpression of Xenopus Aur-A transformed NIH 3T3 cells and led to tumors in nude mice. These results provide further evidence that Xenopus Aur-A is a functional ortholog of human Aur-A and, along with the recently described crystal structure of human Aur-A, should help in future studies of the mechanisms that regulate Aur-A activity during mitotic progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of a new APC/C recognition domain, the A box, which is required for the Cdh1-dependent destruction of the kinase Aurora-A during mitotic exit.Genes Dev. 2002 Sep 1;16(17):2274-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1007302. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12208850 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for the destruction of human Aurora-A.J Cell Sci. 2004 Dec 1;117(Pt 25):5975-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01418. Epub 2004 Nov 9. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15536123
-
Analysis of mitotic phosphorylation of borealin.BMC Cell Biol. 2007 Jan 22;8:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-8-5. BMC Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17241471 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora A, meiosis and mitosis.Biol Cell. 2004 Apr;96(3):215-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biolcel.2003.09.008. Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15182704 Review.
-
The Aurora kinases: role in cell transformation and tumorigenesis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003 Dec;22(4):451-64. doi: 10.1023/a:1023789416385. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003. PMID: 12884918 Review.
Cited by
-
Aurora A selective inhibitor MLN8237 suppresses the growth and survival of HTLV-1-infected T-cells in vitro.Cancer Sci. 2010 May;101(5):1204-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01499.x. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20180813 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora kinase inhibitor ZM447439 blocks chromosome-induced spindle assembly, the completion of chromosome condensation, and the establishment of the spindle integrity checkpoint in Xenopus egg extracts.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1305-18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0891. Epub 2004 Dec 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15616188 Free PMC article.
-
CHD1, a multifaceted epigenetic remodeler in prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 26;13:1123362. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1123362. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36776288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora-A site specificity: a study with synthetic peptide substrates.Biochem J. 2005 Aug 15;390(Pt 1):293-302. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050343. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 16083426 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) interacts with signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) in activating Aurora-A gene expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Aug;36(13):4337-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn417. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18586824 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

