Influence of gender and interleukin-10 deficiency on the inflammatory response during lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice
- PMID: 12423305
- PMCID: PMC1782799
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01508.x
Influence of gender and interleukin-10 deficiency on the inflammatory response during lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis females have a worse prognosis compared to male patients. Furthermore, cystic fibrosis patients infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa have been shown to have dysregulated cytokine profiles, as higher levels of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin (IL)-8, and lower levels of IL-10 are found in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid compared to healthy controls. The present study was aimed at investigating the importance of gender and IL-10 in the susceptibility of C57BL/6 mice to pulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We found that wildtype females were more susceptible than males to infection, as we observed greater weight loss, higher bacterial load, and inflammatory mediators in their lungs. IL-10 knockout mice, both females and males, had higher levels of TNF-alpha in the lungs compared to wildtype mice and maintained higher levels of polymorphonuclear cells and lower levels of macrophages for a longer period of time. Our results demonstrate that the number of bacteria recovered from the lungs of IL-10 knockout male mice was significantly higher than that observed in their wildtype male counterparts and we show that neutralization of IL-10 in infected female mice for a prolonged period of time leads to increased susceptibility to infection. Results reported in this study clearly demonstrate that females, both wildtype and IL-10 knockout mice are more susceptible to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection than males, and that they mount a stronger inflammatory response in the lungs.
Figures
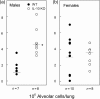
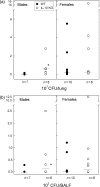
References
-
- Wojnarowski C, Frischer T, Hofbauer E, Grabner C, Mosgoeller W, Eichler I, Ziesche R. Cytokine expression in bronchial biopsies of cystic fibrosis patients with and without acute exacerbation. Eur Respir J. 1999;14:1136–44. - PubMed
-
- Bonfield TL, Konstan MW, Burfeind P, Panuska JR, Hilliard JB, Berger M. Normal bronchial epithelial cells constitutively produce the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10, which is downregulated in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995;13:257–61. - PubMed
-
- Bonfield TL, Panuska JR, Konstan MW, Hilliard KA, Hilliard JB, Ghnaim H, Berger M. Inflammatory cytokines in cystic fibrosis lungs [published erratum appears in Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 154: 1217] Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:2111–8. - PubMed
-
- Dosanjh AK, Elashoff D, Robbins RC. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of cystic fibrosis lung transplant recipients demonstrates increased interleukin-8 and elastase and decreased IL-10. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998;18:851–54. - PubMed
-
- Massengale AR, Quinn FJ, Yankaskas J, Weissman D, McClellan WT, Cuff C, Aronoff SC. Reduced interleukin-8 production by cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;20:1073–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

