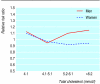
Risk factor thresholds. Threshold is 37 000 pounds sterling per QALY
- PMID: 12424179
- PMCID: PMC1124591
Risk factor thresholds. Threshold is 37 000 pounds sterling per QALY
Figures
Comment on
-
Risk factor thresholds: their existence under scrutiny.BMJ. 2002 Jun 29;324(7353):1570-6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7353.1570. BMJ. 2002. PMID: 12089098 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources