RNA editing by ADARs is important for normal behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 12426375
- PMCID: PMC137199
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf607
RNA editing by ADARs is important for normal behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
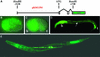
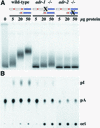
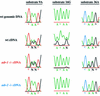
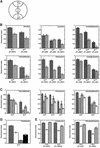
Here we take advantage of the well-characterized and simple nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans to further our understanding of the functions of RNA editing. We describe the two C.elegans ADAR genes, adr-1 and adr-2, and characterize strains containing homozygous deletions in each, or both, of these genes. We find that adr-1 is expressed in most, if not all, cells of the C.elegans nervous system and also in the developing vulva. Using chemotaxis assays, we show that both ADARs are important for normal behavior. Biochemical, molecular and phenotypic analyses indicate that ADR-1 and ADR-2 have distinct roles in C.elegans, but sometimes act together.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson P. (1995) Mutagenesis. In Epstein,H. and Shakes,D. (eds), Caenorhabditis elegans: Modern Biological Analysis of an Organism. Vol. 48. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp. 31–58.
-
- Baltimore D. (2001) Our genome unveiled. Nature, 409, 814–816. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann C.I. and Kaplan,J.M. (1998) Signal transduction in the Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 21, 279–308. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann C.I., Hartwieg,E. and Horvitz,H.R. (1993) Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C.elegans. Cell, 74, 515–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

