The double-edged sword of COX-2 selective NSAIDs
- PMID: 12427705
- PMCID: PMC134294
The double-edged sword of COX-2 selective NSAIDs
Abstract
The launch of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) selective NSAIDs was based on 2 hypotheses: (1) the major adverse effects limiting the usefulness of nonselective NSAIDs are gastrointestinal in nature and (2) COX-2 selective NSAIDs are associated with fewer gastrointestinal adverse effects than nonselective NSAIDs. At the time of the launch, neither of these hypotheses had been proven and, as documented in this review, both remain uncertain. The increased incidence of total and nongastrointestinal serious adverse events, with the COX-2 selective NSAIDs as compared with nonselective NSAIDs, in the Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study (CLASS) and the Vioxx Gastrointestinal Outcomes Research (VIGOR) study remains a major concern. The increased morbidity associated with the COX-2 selective NSAIDs may be a manifestation of the COX-2 selectivity of rofecoxib and celecoxib or the supramaximal doses of these drugs used in the trials. Proof that the increased harm was not caused by the COX-2 selectivity of the drugs depends on demonstration in a randomized controlled trial that COX-2 selective NSAIDs at usual doses are as effective as nonselective NSAIDs and cause fewer gastrointestinal serious adverse events without increasing the incidence of total nongastrointestinal serious adverse events.
Figures
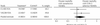
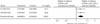
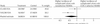
Comment in
-
Seeking disclosure.CMAJ. 2003 Apr 15;168(8):960, 962; author reply 962. CMAJ. 2003. PMID: 12695369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COX-2 inhibitors and type 4 error.CMAJ. 2003 Aug 5;169(3):190. CMAJ. 2003. PMID: 12900475 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lipsky PE. Progress toward a new class of therapeutics: selective COX-2 inhibition. J Rheumatol 1997;24(Suppl 49):1-8.
-
- Lane NE. Pain management in osteoarthritis: the role of COX-2 inhibitors. J Rheumatol 1997;24(Suppl 49):20-4. - PubMed
-
- Celecoxib (Celebrex): Is it a breakthrough drug? Ther Lett 1999;31:1-2. Available: www.ti.ubc.ca/pages/letter31.htm (accessed 2002 Sept 12)
-
- Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL, Simon LS, Pincus T, Whelton A, et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2000;284:1247-55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
