A synaptic explanation of suppression in visual cortex
- PMID: 12427863
- PMCID: PMC6757815
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-22-10053.2002
A synaptic explanation of suppression in visual cortex
Abstract
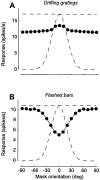
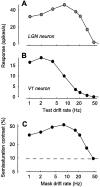
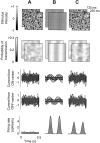
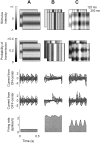
The responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex (V1) are suppressed by mask stimuli that do not elicit responses if presented alone. This suppression is widely believed to be mediated by intracortical inhibition. As an alternative, we propose that it can be explained by thalamocortical synaptic depression. This explanation correctly predicts that suppression is monocular, immune to cortical adaptation, and occurs for mask stimuli that elicit responses in the thalamus but not in the cortex. Depression also explains other phenomena previously ascribed to intracortical inhibition. It explains why responses saturate at high stimulus contrast, whereas selectivity for orientation and spatial frequency is invariant with contrast. It explains why transient responses to flashed stimuli are nonlinear, whereas spatial summation is primarily linear. These results suggest that the very first synapses into the cortex, and not the cortical network, may account for important response properties of V1 neurons.
Figures
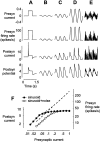

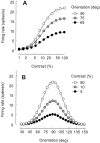
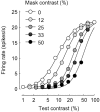
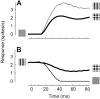
References
-
- Abbott LF, Varela JA, Sen K, Nelson SB. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science. 1997;275:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht DG. Visual cortex neurons in monkey and cat: effect of contrast on the spatial and temporal phase transfer functions. Vis Neurosci. 1995;12:1191–1210. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht DG, Geisler WS. Motion sensitivity and the contrast-response function of simple cells in the visual cortex. Vis Neurosci. 1991;7:531–546. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht DG, Hamilton DB. Striate cortex of monkey and cat: contrast response function. J Neurophysiol. 1982;48:217–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
