Motility determinants in WASP family proteins
- PMID: 12429845
- PMCID: PMC133613
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0294
Motility determinants in WASP family proteins
Abstract
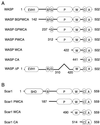
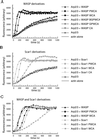
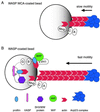
In response to upstream signals, proteins in the Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASP) family regulate actin nucleation via the Arp2/3 complex. Despite intensive study of the function of WASP family proteins in nucleation, it is not yet understood how their distinct structural organization contributes to actin-based motility. Herein, we analyzed the activities of WASP and Scar1 truncation derivatives by using a bead-based motility assay. The minimal region of WASP sufficient to direct movement was the C-terminal WCA fragment, whereas the corresponding region of Scar1 was insufficient. In addition, the proline-rich regions of WASP and Scar1 and the Ena/VASP homology 1 (EVH1) domain of WASP independently enhanced motility rates. The contributions of these regions to motility could not be accounted for by their direct effects on actin nucleation with the Arp2/3 complex, suggesting that they stimulate motility by recruiting additional factors. We have identified profilin as one such factor. WASP- and Scar1-coated bead motility rates were significantly reduced by depletion of profilin and VASP and could be more efficiently rescued by a combination of VASP and wild-type profilin than by VASP and a mutant profilin that cannot bind proline-rich sequences. Moreover, motility of WASP WCA beads was not affected by the depletion or addback of VASP and profilin. Our results suggest that recruitment of factors, including profilin, by the proline-rich regions of WASP and Scar1 and the EVH1 domain of WASP stimulates cellular actin-based motility.
Figures




References
-
- Anton IM, Lu W, Mayer BJ, Ramesh N, Geha RS. The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein-interacting protein (WIP) binds to the adaptor protein Nck. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:20992–20995. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann C, Fischer L, Walter U, Reinhard M. The EVH2 domain of the vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein mediates tetramerization, F-actin binding, and actin bundle formation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:23549–23557. - PubMed
-
- Bear JE, Krause M, Gertler FB. Regulating cellular actin assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:158–166. - PubMed
-
- Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, Maly IM, Chaga OY, Cooper JA, Borisy GG, Gertler FB. Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell. 2002;109:509–524. - PubMed
-
- Bernheim-Groswasser A, Wiesner S, Golsteyn RM, Carlier MF, Sykes C. The dynamics of actin-based motility depend on surface parameters. Nature. 2002;417:308–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

