A chromosomal position effect on gene targeting in human cells
- PMID: 12433992
- PMCID: PMC137162
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf614
A chromosomal position effect on gene targeting in human cells
Abstract
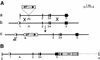
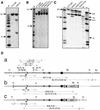
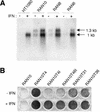
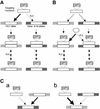
We describe gene targeting experiments involving a human cell line (RAN10) containing, in addition to its endogenous alleles, two ectopic alleles of the interferon-inducible gene 6-16. The frequency of gene targeting at one of the ectopic 6-16 alleles (H3.7) was 34-fold greater than the combined frequency of gene targeting involving endogenous 6-16 alleles in RAN10. Preference for H3.7 was maintained when the target loci in RAN10 were transcriptionally activated by interferon. Despite the 34-fold preference for H3.7, the absolute gene targeting efficiency in RAN10 was only 3-fold higher than in the parental HT1080 cell line. These data suggest that different alleles can compete with each other, and perhaps with non-homologous loci, in a step which is necessary, but not normally rate-limiting, for gene targeting. The efficiency of this step can therefore be more sensitive to chromosomal position effects than the rate-determining steps for gene targeting. The nature of the position effects involved remains unknown but does not correlate with transcription status, which in our system has a very modest influence on the frequency of gene targeting. In summary, our work unequivocally identifies a position effect on gene targeting in human cells.
Figures

References
-
- Festenstein R. and Kioussis,D. (2000) Locus control regions and epigenetic chromatin modifiers. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 10, 199–203. - PubMed
-
- Cappechi M.R. (1989) Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science, 244, 1288–1292. - PubMed
-
- Smithies O., Koralewski,M.A., Song,K.Y. and Kucherlapati,R.S. (1984) Homologous recombination with DNA introduced into mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 49, 161–170. - PubMed
-
- Haber J.E. (2000) Partners and pathways repairing a double-strand break. Trends Genet., 16, 259–264. - PubMed
-
- van Gent D.C., Hoeijmakers,J.H. and Kanaar,R. (2001) Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nature Rev. Genet., 2, 196–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

