Potential role of p53 on metallothionein induction in human epithelial breast cancer cells
- PMID: 12434295
- PMCID: PMC2364318
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600549
Potential role of p53 on metallothionein induction in human epithelial breast cancer cells
Abstract
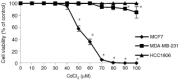
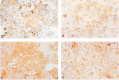
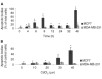
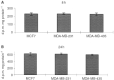
The expression and induction of metallothionein has been associated with protection against oxidative stress and apoptosis. This study examines the effect of tumour suppressor protein p53 on metallothionein expression following CdCl2 treatment in eight human epithelial breast cancer cell lines differing in p53 and oestrogen-receptor status. Cells were treated with 10 microM CdCl2 for 24 h and metallothionein protein levels were measured by cadmium binding assay. MCF7 cells which are p53-positive (p53+) and oestrogen-receptor-positive showed a large induction in metallothionein synthesis by 10.79+/-1.36-fold. Other breast cancer cell lines which are p53-negative (p53-) and oestrogen-receptor-negative or weakly oestrogen-receptor-positive showed a small induction ranging from 1.40+/-0.10 to 3.65+/-0.30-fold. RT-PCR analysis showed an induction of metallothionein mRNA in MCF7 cells by about 1.61+/-0.08-fold, while in HCC1806 cells (p53-, oestrogen-receptor-negative) by 1.11+/-0.13-fold, and in MDA-MB-231 (p53-, oestrogen-receptor-negative) by 1.25+/-0.06-fold. Metallothionein localisation was determined by immunohistochemical staining. Prior to metal treatment, metallothionein was localised mainly in the cytoplasm of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. After treatment with 10 microM CdCl2 for 24 h, MCF7 cells showed intense nuclear and cytoplasmic staining for metallothionein, while MDA-MB-231 cells showed staining in the cytoplasm with weak nuclear staining. Apoptosis induced by 10-40 microM CdCl2 at time points between 4 and 48 h was examined with TUNEL assay. In MCF7 cells, apoptosis increased with higher concentrations of CdCl2, it peaked at 6-8 h and appeared again at 48 h for all concentrations of CdCl2 tested. In MDA-MB-231 cells, apoptosis remained at low levels for 10-40 microM CdCl2 at all time points. Studies on cadmium uptake showed similar uptake and accumulation of cadmium at 8 and 24 h in all the cell lines. The data demonstrate that treatment of epithelial breast cancer cells with 10 microM CdCl2 for 24 h caused a greater induction of metallothionein protein and mRNA expression in p53+ and oestrogen-receptor-positive cells as compared to p53- and oestrogen-receptor-negative or weakly oestrogen-receptor-positive cells. This effect may be associated with the occurrence of apoptosis and suggests a role for p53 and oestrogen-receptor on the expression and induction of metallothionein in epithelial cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metallothionein 1E mRNA is highly expressed in oestrogen receptor-negative human invasive ductal breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2000 Aug;83(3):319-23. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1276. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10917545 Free PMC article.
-
Basal and copper-induced expression of metallothionein isoform 1,2 and 3 genes in epithelial cancer cells: The role of tumor suppressor p53.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2016 May;35:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27049123
-
Metallothionein isoform expression by breast cancer cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;32(8):895-903. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(00)00024-8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10940647
-
Stable transfection and overexpression of metallothionein isoform 3 inhibits the growth of MCF-7 and Hs578T cells but not that of T-47D or MDA-MB-231 cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003 Jul;80(2):181-91. doi: 10.1023/A:1024520801262. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003. PMID: 12908821
-
Differential expression of metallothionein 1 and 2 isoforms in breast cancer lines with different invasive potential: identification of a novel nonsilent metallothionein-1H mutant variant.Am J Pathol. 2003 Nov;163(5):2009-19. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63559-6. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14578200 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of gene expression profiling reveals novel basal gene signatures in MCF-10A cells transformed with cadmium.Oncotarget. 2020 Sep 29;11(39):3601-3617. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27734. eCollection 2020 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 33062196 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of the transcription factors snail and slug alters the response to genotoxic stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(17):7559-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7559-7566.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314165 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium Impairs p53 Activity in HepG2 Cells.ISRN Toxicol. 2014 Mar 13;2014:976428. doi: 10.1155/2014/976428. eCollection 2014. ISRN Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25101185 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Expression Analysis: Cell Lines HCC1500 and HCC1937 as Models for Breast Cancer in Young Women and the miR-23a as a Poor Prognostic Biomarker.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2020 Dec 2;14:1178223420977845. doi: 10.1177/1178223420977845. eCollection 2020. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2020. PMID: 33311984 Free PMC article.
-
Altered-function p53 missense mutations identified in breast cancers can have subtle effects on transactivation.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 May;8(5):701-16. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0442. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20407015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Abdel-MageedABAgrawalKC1997Antisense down-regulation of metallothionein induces growth arrest and apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cells Cancer Gene Ther 4199207 - PubMed
-
- AgarwalMLTaylorWRChernovMVChernovaOBStarkGR1998The p53 network J Biol Chem 27314 - PubMed
-
- AschnerMConklinDRYaoCPAllenJWTanKH1998Induction of astrocyte metallothioneins (MTs) by zinc confers resistance against the acute cytotoxic effects of methylmercury on cell swelling, Na+ uptake, and K+ release Brain Res 813254261 - PubMed
-
- CaiLKoropatnickJCherianMG1995Metallothioneins protect DNA from copper-induced but not iron-induced cleavage in vitro Chem Biol Interact 96143155 - PubMed
-
- CaiLKoropatnickJCherianMG1996Metallothionein and DNA damageInBiological Effects of Low Level Ionizing Radiation and Molecular Biology ResearchGong SL (ed)pp7788Chanchun: Norman Bethune University of Medical Sciences
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

