Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type I is caused by mutations in codanin-1
- PMID: 12434312
- PMCID: PMC378595
- DOI: 10.1086/344781
Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type I is caused by mutations in codanin-1
Abstract
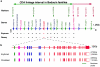
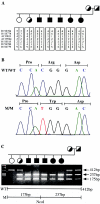
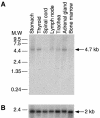
Congenital dyserythropoietic anemias (CDAs) constitute a rare group of inherited red-blood-cell disorders associated with dysplastic changes in late erythroid precursors. CDA type I (CDAI [MIM 224120], gene symbol CDAN1) is characterized by erythroid pathological features such as internuclear chromatin bridges, spongy heterochromatin, and invagination of the nuclear membrane, carrying cytoplasmic organelles into the nucleus. A cluster of 45 highly inbred Israeli Bedouin with CDAI enabled the mapping of the CDAN1 disease gene to a 2-Mb interval, now refined to 1.2 Mb, containing 15 candidate genes on human chromosome 15q15 (Tamary et al. 1998). After the characterization and exclusion of 13 of these genes, we identified the CDAN1 gene through 12 different mutations in 9 families with CDAI. This 28-exon gene, which is transcribed ubiquitously into 4738 nt mRNA, was reconstructed on the basis of gene prediction and homology searches. It encodes codanin-1, a putative o-glycosylated protein of 1,226 amino acids, with no obvious transmembrane domains. Codanin-1 has a 150-residue amino-terminal domain with sequence similarity to collagens and two shorter segments that show weak similarities to the microtubule-associated proteins, MAP1B (neuraxin) and synapsin. These findings, and the cellular phenotype, suggest that codanin-1 may be involved in nuclear envelope integrity, conceivably related to microtubule attachments. The specific mechanisms by which codanin-1 underlies normal erythropoiesis remain to be elucidated.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (for codanin-1 homologs and orthologs, as well as genetic markers)
-
- Blocks, http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/blocks/ (for biological sequence analysis) (Henikoff et al. 2000)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for KIAA0770 [AB018313], DKFZP564G2022 [NM_015497], ZFP106 [NM_022473], SNAP23 [NM_003825], FLJ10460 [NM_018097], FLJ23375 [NM_024956], CCNDBP1 [NM_012142], EPB42 [NM_000119], TGM5 [NM_004245], UBR1 [AF525401], TTBK [AF525400], FLJ008 [AF525397], CDANI [AF525398], LOC146050 [AF525399], and vanaso [AF487678S2])
-
- Local Alignment of Multiple Alignment (LAMA), http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/blocks-bin/LAMA_search.sh (for sequence motifs search) (Pietrokovski 1996)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for CDAI [MIM 224120], CDAII [MIM 224100], and CDAIII [MIM 105600])
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Bitner-Glindzicz M, Lindley KJ, Rutland P, Blaydon D, Smith VV, Milla PJ, Hussain K, Furth-Lavi J, Cosgrove KE, Shepherd RM, Barnes PD, O'Brien RE, Farndon PA, Sowden J, Liu XZ, Scanlan MJ, Malcolm S, Dunne MJ, Aynsley-Green A, Glaser B (2000) A recessive contiguous gene deletion causing infantile hyperinsulinism, enteropathy and deafness identifies the Usher type 1C gene. Nat Genet 26:56–60 - PubMed
-
- Delaunay J, Iolascon A (1999) The congenital dyserythropoietic anaemias. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 12:691–705 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

