The roles of individual eukaryotic translation initiation factors in ribosomal scanning and initiation codon selection
- PMID: 12435632
- PMCID: PMC187480
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1020902
The roles of individual eukaryotic translation initiation factors in ribosomal scanning and initiation codon selection
Abstract
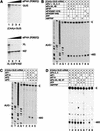
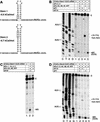
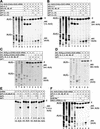
To elucidate an outline of the mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation, 48S complex formation was analyzed on defined mRNAs in reactions reconstituted in vitro from fully purified translation components. We found that a ribosomal 40S subunit, eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 3, and the eIF2 ternary complex form a 43S complex that can bind to the 5'-end of an unstructured 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) and in the presence of eIF1 scan along it and locate the initiation codon without a requirement for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or factors (eIF4A, eIF4B, eIF4F) associated with ATP hydrolysis. Scanning on unstructured 5'-UTRs was enhanced by ATP, eIFs 4A and 4B, and the central domain of the eIF4G subunit of eIF4F. Their omission increased the dependence of scanning on eIFs 1 and 1A. Ribosomal movement on 5'-UTRs containing even weak secondary structures required ATP and RNA helicases. eIF4F was essential for scanning, and eIFs 4A and 4B were insufficient to promote this process in the absence of eIF4F. We report that in addition to its function in scanning, eIF1 also plays a principal role in initiation codon selection. In the absence of eIF1, 43S complexes could no longer discriminate between cognate and noncognate initiation codons or sense the nucleotide context of initiation codons and were able to assemble 48S complexes on 5'-proximal AUG triplets located only 1, 2, and 4 nt from the 5'-end of mRNA.
Figures





References
-
- Anthony DD, Merrick WC. Analysis of 40S and 80S complexes with mRNA as measured by sucrose density gradients and primer extension inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1554–1562. - PubMed
-
- Battiste JL, Pestova TV, Hellen CUT, Wagner G. The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function. Mol Cell. 2000;5:109–119. - PubMed
-
- Carberry SE, Goss DJ. Interaction of wheat germ protein synthesis initiation factors eIF-3, eIF-(iso)4F, and eIF-4F with mRNA analogues. Biochemistry. 1991;30:6977–6982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
