Lactoferrin protects rabbits from Shigella flexneri-induced inflammatory enteritis
- PMID: 12438385
- PMCID: PMC132992
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.7050-7053.2002
Lactoferrin protects rabbits from Shigella flexneri-induced inflammatory enteritis
Abstract
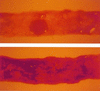
Shigella species cause bacillary dysentery in humans by invasion, intracellular multiplication, spread to adjacent cells, and induction of brisk inflammatory responses in the intestinal epithelium. In vitro data suggest that lactoferrin, a glycoprotein present in human mucosal secretions, has a role in protection from bacterial enteric infections. We sought to determine the activity of lactoferrin in vivo, using the concentration present in human colostrum, to investigate its effect on the development of clinical and pathological evidence of inflammation in a rabbit model of enteritis. Lactoferrin protected rabbits infected with Shigella flexneri from developing inflammatory intestinal disease. Typical histological changes in ill animals included villous blunting with sloughing of epithelial cells, submucosal edema, infiltration of leukocytes, venous congestion, and hemorrhage. Lactoferrin at a concentration normally found in human colostrum blocks development of S. flexneri-induced inflammatory enteritis.
Figures

References
-
- Adler, B., C. Sasakawa, T. Tobe, S. Makino, K. Komatsu, and M. A. Yoshikawa. 1989. Dual transcriptional activation system for the 230 kb plasmid genes coding for virulence-associated antigens of Shigella flexneri. Mol. Microbiol. 3:627-635. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, F., J. D. Clemens, M. R. Rao, D. A. Sack, M. R. Khan, and E. Haque. 1992. Community based evaluation of the effect of breast feeding on the risk of microbiologically confirmed or clinically presumptive shigellosis in Bangladeshi children. Pediatrics 90:406-411. - PubMed
-
- Arnold, R. R., M. F. Cole, and J. R. McGhee. 1977. A bactericidal effect for human lactoferrin. Science 197:263-265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

