Elevated levels of circulating interleukin-18 in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals: role of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and implications for AIDS pathogenesis
- PMID: 12438570
- PMCID: PMC136707
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.24.12448-12456.2002
Elevated levels of circulating interleukin-18 in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals: role of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and implications for AIDS pathogenesis
Abstract
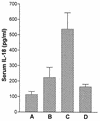
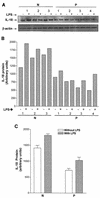
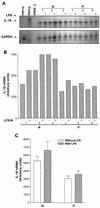
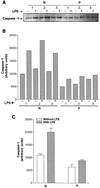
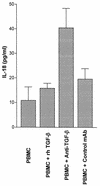
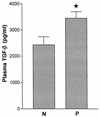
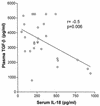
Originally identified as the gamma interferon-inducing factor, interleukin-18 (IL-18) was rediscovered as a proinflammatory cytokine related to the IL-1 family of cytokines that plays an important role in both innate and adaptive immune responses against viruses and intracellular pathogens. Despite its importance in inducing and regulating immune responses, relatively little is known about its production in HIV infection. We report here significantly (P < 0.05) elevated levels of this cytokine in the sera of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected/AIDS patients compared to those of HIV-seronegative healthy persons. Surprisingly, the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from HIV-infected/AIDS patients were compromised in the ability to upregulate IL-18 gene expression and produce this cytokine with and without lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. A significant positive correlation (P < 0.05) existed between the concentration of IL-18 in serum and its production from PBMC of HIV-seronegative healthy individuals but not those of HIV-infected/AIDS patients. Furthermore, the patients' PBMC expressed relatively reduced levels of activated caspase-1 constitutively as well as in response to LPS stimulation. Our data suggest the involvement of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in suppressing IL-18 production from the patients' PBMC for the following reasons. (i) In in vitro studies it suppressed the production of IL-18 from PBMC. (ii) Its levels were significantly higher in the plasma of patients compared to that of control subjects. (iii) A significant negative correlation existed between the concentrations of TGF-beta in plasma and of IL-18 in serum of the patients. The elevated levels of IL-18 in the serum of HIV-infected individuals may contribute to AIDS pathogenesis, whereas its compromised production from their PBMC in response to stimuli may reduce their innate defense to opportunistic intracellular pathogens.
Figures
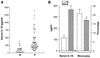
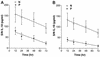
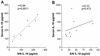
References
-
- Ahmad, A., R. Ahmad, E. Toma, R. Morisset, and J. Menezes. 2000. Impaired induction of IL-15 in response to herpes simplex virus type 1 infection in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of HIV-infected patients. AIDS 14:744-746. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad, R., L. Knafo, J. Xu, S. T. Sindhu, J. Menezes, and A. Ahmad. 2000. Thrombin induces apoptosis in human tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 87:707-715. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S. 2000. The role of IL-18 in innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 12:59-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

