Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer
- PMID: 12439907
- PMCID: PMC4656400
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.966
Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expression in esophageal cancer
Abstract
Aim: Esophageal carcinoma is one of the most common malignant tumors in China. But the molecular mechanisms of esophageal carcinoma remains unclear. Gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor (GKLF) is a newly identified transcription factor which is expressed abandantly in the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and deregulation of GKLF was linked to several types of cancer. It is of interest to study the expression and role of GKLF in esophageal carcinoma.
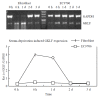
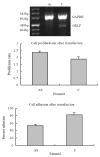
Methods: Semi-quantitative RT-PCR was used to compare GKLF expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to normal mucosa of the same patients. The serum deprivation inducibility of GKLF was observed in an esophageal squamous cancer cell line by comparison to the primary culture of human fibroblast. The effect of antisense GKLF transfection on the proliferation and adhesion of esophageal squamous cancer cell line was also observed.
Results: The level of GKLF transcript is lower in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma compared to paired normal-appearing mucosa in 14 of 17 of the tumors analyzed. The serum deprivation inducibility of GKLF was greatly decreased in an esophageal squamous cancer cell line compared to the primary culture of human fibroblast. Decreased expression of GKLF in the esophageal cancer cell by antisense GKLF transfection increased its proliferation rate compared with that of vector transfected cell control (P<0.05). Transfection of antisense GKLF decreased its adhesion ability (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The findings of this study demonstrate the down-regulation of GKLF in esophageal squamous cancer, and suggest that deregulation of GKLF may play a role in initiation and/or progression as well as the metastasis of esophageal squamous cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. A gene for a novel zinc-finger protein expressed in differentiated epithelial cells and transiently in certain mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31384–31390. - PubMed
-
- Yet SF, McA'Nulty MM, Folta SC, Yen HW, Yoshizumi M, Hsieh CM, Layne MD, Chin MT, Wang H, Perrella MA, et al. Human EZF, a Krüppel-like zinc finger protein, is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and contains transcriptional activation and repression domains. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1026–1031. - PubMed
-
- Segre JA, Bauer C, Fuchs E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat Genet. 1999;22:356–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

