Redox-dependent structural changes in archaeal and bacterial Rieske-type [2Fe-2S] clusters
- PMID: 12441394
- PMCID: PMC2373747
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0222402
Redox-dependent structural changes in archaeal and bacterial Rieske-type [2Fe-2S] clusters
Abstract
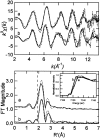
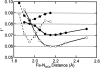
Proteins containing Rieske-type [2Fe-2S] clusters play important roles in many biological electron transfer reactions. Typically, [2Fe-2S] clusters are not directly involved in the catalytic transformation of substrate, but rather supply electrons to the active site. We report herein X-ray absorption spectroscopic (XAS) data that directly demonstrate an average increase in the iron-histidine bond length of at least 0.1 A upon reduction of two distantly related Rieske-type clusters in archaeal Rieske ferredoxin from Sulfolobus solfataricus strain P-1 and bacterial anthranilate dioxygenases from Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1. This localized redox-dependent structural change may fine tune the protein-protein interaction (in the case of ARF) or the interdomain interaction (in AntDO) to facilitate rapid electron transfer between a lower potential Rieske-type cluster and its redox partners, thereby regulating overall oxygenase reactions in the cells.
Figures
References
-
- Berry, E.A., Guergova-Kuras, M., Huang, L.-S., and Crofts, A.R. 2000. Structure and function of cytochrome bc complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69 1005–1075. - PubMed
-
- Brugna, M., Nitschke, W., Asso, M., Guigliarelli, B., Lemesle-Meunier, D., and Schmidt, C. 1999. Redox components of cytochrome bc-type enzymes in acidophilic prokaryotes. II. The Rieske protein of phylogenetically distant acidophilic organisms. J. Biol. Chem. 274 16766–16772. - PubMed
-
- Carrell, C.J., Zhang, H., Cramer, W.A., and Smith, J.L. 1997. Biological identity and diversity in photosynthesis and respiration: Structure of the lumen-side domain of the chloroplast Rieske protein. Structure 5 1613–1625. - PubMed
-
- Cline, J.F., Hoffman, B.M., Mims, W.B., LaHaie, E., Ballou, D.P., and Fee, J.A. 1985. Evidence for N coordination to Fe in the [2Fe-2S] clusters of Thermus Rieske protein and phthalate dioxygenase from Pseudomonas. J. Biol. Chem. 260 3251–3254. - PubMed
-
- Colbert, C.L., Couture, M.M.-J., Eltis, L.D., and Bolin, J. 2000. A cluster exposed: Structure of the Rieske ferredoxin from biphenyl dioxygenase and the redox properties of Rieske Fe-S proteins. Structure 8 1267–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

