Host-pathogen interactions: Host resistance factor Nramp1 up-regulates the expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 virulence genes
- PMID: 12441401
- PMCID: PMC137780
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252415599
Host-pathogen interactions: Host resistance factor Nramp1 up-regulates the expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 virulence genes
Abstract
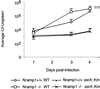
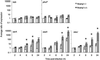
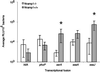
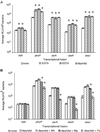
Nramp1 (Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein-1; also known as Slc11a1) is a host resistance gene that provides protection against several intracellular pathogens, including Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Little is known about the dynamic interplay that occurs between mammalian host resistance determinants such as Nramp1 and pathogens during infection. To explore these interactions, we examined the effect of Nramp1 on expression of Salmonella typhimurium (STM) virulence factors. We demonstrate that Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2) is essential for replication of STM in spleens of infected Nramp1(+/+) mice. Furthermore, the presence of Nramp1 in transfected cell lines and congenic knockout mice resulted in the up-regulation of STM SPI2-associated virulence genes critical for intramacrophage survival. This Nramp1-dependent up-regulation of SPI2 was mimicked in vitro by chelation of iron, demonstrating the iron-responsive nature of expression of STM SPI2-associated virulence genes. We propose that acquisition of SPI2 by S. enterica not only enabled this bacterium to become an effective intracellular pathogen but also allowed the bacterium to withstand the effects of macrophage defense mechanisms such as Nramp1 early in the evolution of its pathogenic character. These dynamic Nramp1-pathogen interactions may be essential for regulating the course of an infection. This study demonstrates the presence of a previously undescribed direct influence of a mammalian innate host resistance locus on a pathogen at the genetic level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Removal of the phage-shock protein PspB causes reduction of virulence in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium independently of NRAMP1.J Med Microbiol. 2014 Jun;63(Pt 6):788-795. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.072223-0. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24713356
-
Proteomic analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium isolated from RAW 264.7 macrophages: identification of a novel protein that contributes to the replication of serovar typhimurium inside macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 29;281(39):29131-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604640200. Epub 2006 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16893888
-
SseL is a salmonella-specific translocated effector integrated into the SsrB-controlled salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system.Infect Immun. 2007 Feb;75(2):574-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00985-06. Epub 2006 Dec 11. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17158898 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella pathogenicity islands in host specificity, host pathogen-interactions and antibiotics resistance of Salmonella enterica.Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007 Jul-Aug;120(7-8):317-27. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007. PMID: 17715824 Review.
-
Cellular microbiology of intracellular Salmonella enterica: functions of the type III secretion system encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 2.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Nov;61(22):2812-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4248-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15558211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of small RNA RaoN on nitrosative-oxidative stress resistance and virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Microbiol. 2020 Jun;58(6):499-506. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0027-2. Epub 2020 Apr 11. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32279276
-
Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strategies for Host Adaptation.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 12;8:1983. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01983. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29075247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nramp1AA genotype confers susceptibility to Brucella abortus in water buffalo.Mamm Genome. 2007 Feb;18(2):137-43. doi: 10.1007/s00335-006-0103-x. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Mamm Genome. 2007. PMID: 17334658
-
Quantitative PCR-based competitive index for high-throughput screening of Salmonella virulence factors.Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):360-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00873-10. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21041489 Free PMC article.
-
The intracellular parasite Anncaliia algerae induces a massive miRNA down-regulation in human cells.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 May 18;8(3):363-375. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.05.003. eCollection 2023 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37275245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

