Pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, after morning or evening administration in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 12445025
- PMCID: PMC1874466
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01688.x
Pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, after morning or evening administration in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Aims: To compare the lipid-regulating effects and steady-state pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, a new synthetic hydroxy methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor, following repeated morning and evening administration in volunteers with fasting serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations < 4.14 mmol l-1.
Methods: In this open-label two-way crossover trial 24 healthy adult volunteers were randomized to receive rosuvastatin 10 mg orally each morning (07.00 h) or evening (18.00 h) for 14 days. After a 4 week washout period, volunteers received the alternative regimen for 14 days. Rosuvastatin was administered in the absence of food.
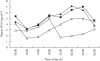
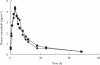
Results: Reductions from baseline in serum concentrations of LDL-C (-41.3%[morning]vs-44.2%[evening]), total cholesterol (-30.9%vs-31.8%), triglycerides (-17.1%vs-22.7%), and apolipoprotein B (-32.4%vs-35.3%) were similar following morning and evening administration. AUC(0,24 h) for plasma mevalonic acid (MVA), an in vivo marker of HMG-CoA reductase activity, decreased by -29.9% (morning) vs-32.6% (evening). Urinary excretion of MVA declined by -33.6% (morning) vs-29.2% (evening). The steady-state pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin were very similar following the morning and evening dosing regimens. The Cmax values were 4.58 vs 4.54 ng ml-1, and AUC(0,24 h) values were 40.1 vs 42.7 ng ml-1 h, following morning and evening administration, respectively. There were no serious adverse events during the trial, and rosuvastatin was well tolerated after morning and evening administration.
Conclusions: The pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin are not dependent on time of dosing. Morning or evening administration is equally effective in lowering LDL-C.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetic properties of rosuvastatin after single-dose, oral administration in Chinese volunteers: a randomized, open-label, three-way crossover study.Clin Ther. 2007 Oct;29(10):2194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.10.005. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18042475 Clinical Trial.
-
A double-blind, randomized, incomplete crossover trial to assess the dose proportionality of rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers.Clin Ther. 2003 Aug;25(8):2215-24. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80214-x. Clin Ther. 2003. PMID: 14512129 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of erythromycin on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003 May;59(1):51-6. doi: 10.1007/s00228-003-0573-7. Epub 2003 Apr 1. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12682802 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic aspects of rosuvastatin.J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Sep;42(9):963-70. J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12211221 Review.
-
[Pharmacologic characteristics of rosuvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor].Therapie. 2003 Mar-Apr;58(2):113-21. doi: 10.2515/therapie:2003016. Therapie. 2003. PMID: 12942850 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Tailoring of Rosuvastatin Calcium and Atenolol Bilayer Tablets for the Management of Hyperlipidemia Associated with Hypertension: A Preclinical Study.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 4;14(8):1629. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081629. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015255 Free PMC article.
-
A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interaction between rosuvastatin and valsartan in healthy subjects.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 2;9:745-52. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76942. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25767372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of statins in lung cancer.Arch Med Sci. 2021 Mar 18;18(1):141-152. doi: 10.5114/aoms/123225. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35154535 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of multiple-dose rosuvastatin: An open-label, randomized-sequence, three-way crossover trial in healthy Chinese volunteers.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2009 Oct;70(5):392-404. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2009.10.004. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2009. PMID: 24683247 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Predict OATP1B1-Related Variability in Pharmacodynamics of Rosuvastatin.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 9;3(7):e124. doi: 10.1038/psp.2014.24. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25006781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bucher HC, Griffith LE, Guyatt GH. Systematic review on the risk and benefit of different cholesterol-lowering interventions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:187–195. - PubMed
-
- Knopp RH. Drug treatment of lipid disorders. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:498–511. - PubMed
-
- Rubenfire M, Coletti AT, Mosca L. Treatment strategies for management of serum lipids: lessons learned from lipid metabolism, recent clinical trials, and experience with the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1998;41:95–116. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Salinas CA, Barrett H, Schonfeld G. Metabolic modes of action of the statins in the hyperlipoproteinemias. Atherosclerosis. 1998;141:203–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

