Dynamic behavior of transcription factors on a natural promoter in living cells
- PMID: 12446572
- PMCID: PMC1308318
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf244
Dynamic behavior of transcription factors on a natural promoter in living cells
Abstract
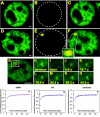
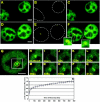
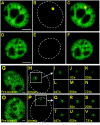
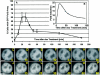
Through the use of photobleaching techniques, we examined the dynamic interaction of three members of the transcription apparatus with a target promoter in living cells. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) interacting protein 1 (GRIP-1) exhibits a half maximal time for fluorescent recovery (tau(R)) of 5 s, reflecting the same rapid exchange as observed for GR. In contrast, the large subunit (RPB1) of RNA polymerase II (pol II) required 13 min for complete fluorescence recovery, consistent with its function as a processive enzyme. We also observe a complex induction profile for the kinetics of GR-stimulated transcription. Our results indicate that GR and GRIP-1 as components of the activating complex are in a dynamic equilibrium with the promoter, and must return to the template many times during the course of transcriptional activation.
Figures
References
-
- Archer T.K., Lee H.-L., Cordingley M.G., Mymryk J.S., Fragoso G., Berard D.S. and Hager G.L. (1994) Differential steroid hormone induction of transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol. Endocrinol., 8, 568–576. - PubMed
-
- Baumann C.T., Ma H., Wolford R.G., Reyes J.C., Maruvada P., Lim C.S., Yen P.M., Stallcup M.R. and Hager G.L. (2001) The glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein 1 (GRIP-1) localizes in discrete nuclear foci that associate with ND10 nuclear bodies and are enriched in components of the 26S proteasome. Mol. Endocrinol., 15, 485–500. - PubMed
-
- Becker P.B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strahle U. and Schutz G. (1986) In vivo protein–DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature, 324, 686–688. - PubMed
-
- Chodosh L.A., Fire A., Samuels M. and Sharp P.A. (1989) 5,6-dichloro-1-β-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. J. Biol. Chem., 264, 2250–2257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

