Nuclear receptor corepressor recruitment by unliganded thyroid hormone receptor in gene repression during Xenopus laevis development
- PMID: 12446772
- PMCID: PMC139868
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8527-8538.2002
Nuclear receptor corepressor recruitment by unliganded thyroid hormone receptor in gene repression during Xenopus laevis development
Abstract
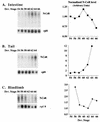
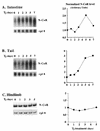
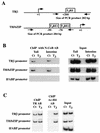
Thyroid hormone receptors (TR) act as activators of transcription in the presence of the thyroid hormone (T(3)) and as repressors in its absence. While many in vitro approaches have been used to study the molecular mechanisms of TR action, their physiological relevance has not been addressed. Here we investigate how TR regulates gene expression during vertebrate postembryonic development by using T(3)-dependent amphibian metamorphosis as a model. Earlier studies suggest that TR acts as a repressor during premetamorphosis when T(3) is absent. We hypothesize that corepressor complexes containing the nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR) are key factors in this TR-dependent gene repression, which is important for premetamorphic tadpole growth. To test this hypothesis, we isolated Xenopus laevis N-CoR (xN-CoR) and showed that it was present in pre- and metamorphic tadpoles. Using a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, we demonstrated that xN-CoR was recruited to the promoters of T(3) response genes during premetamorphosis and released upon T(3) treatment, accompanied by a local increase in histone acetylation. Furthermore, overexpression of a dominant-negative N-CoR in tadpole tail muscle led to increased transcription from a T(3)-dependent promoter. Our data indicate that N-CoR is recruited by unliganded TR to repress target gene expression during premetamorphic animal growth, an important process that prepares the tadpole for metamorphosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recruitment of N-CoR/SMRT-TBLR1 corepressor complex by unliganded thyroid hormone receptor for gene repression during frog development.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;24(8):3337-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3337-3346.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15060155 Free PMC article.
-
A dominant-negative thyroid hormone receptor blocks amphibian metamorphosis by retaining corepressors at target genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):6750-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6750-6758.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972595 Free PMC article.
-
A role of unliganded thyroid hormone receptor in postembryonic development in Xenopus laevis.Mech Dev. 2007 Jul;124(6):476-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.03.006. Mech Dev. 2007. PMID: 17482434 Free PMC article.
-
Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor regulates metamorphic timing via the recruitment of histone deacetylase complexes.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013;105:275-97. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396968-2.00010-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23962846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corepressor requirement and thyroid hormone receptor function during Xenopus development.Vitam Horm. 2004;68:209-30. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)68007-1. Vitam Horm. 2004. PMID: 15193456 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of thyroid hormone-induced adult intestinal stem cell development during anuran metamorphosis.Cell Biosci. 2014 Nov 28;4:73. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-73. eCollection 2014. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25937894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and Mechanism of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Action During Amphibian Development.Endocrinology. 2024 Sep 26;165(11):bqae137. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae137. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39397558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mechanism to Enhance Cellular Responsivity to Hormone Action: Krüppel-Like Factor 9 Promotes Thyroid Hormone Receptor-β Autoinduction During Postembryonic Brain Development.Endocrinology. 2016 Apr;157(4):1683-93. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1980. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26886257 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid-receptor coactivator complexes in thyroid hormone-regulation of Xenopus metamorphosis.Vitam Horm. 2023;123:483-502. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2023.02.003. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Vitam Horm. 2023. PMID: 37717995 Free PMC article.
-
Unliganded progesterone receptor-mediated targeting of an RNA-containing repressive complex silences a subset of hormone-inducible genes.Genes Dev. 2013 May 15;27(10):1179-97. doi: 10.1101/gad.215293.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23699411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alland, L., R. Muhle, Jr., H. Hou, J. Potes, L. Chin, N. Schreiber-Agus, and R. A. DePinho. 1997. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 387:49-55. - PubMed
-
- Almouzni, G., and A. P. Wolffe. 1993. Replication coupled chromatin assembly is required for the repression of basal transcription in vivo. Genes Dev. 7:2033-2047. - PubMed
-
- Burke, L. J., and A. Baniahmad. 2000. Co-repressors 2000: FASEB J. 14:1876-1888. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. D., and R. M. Evans. 1995. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature 377:454-457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
