Signal-transducing adaptor molecules STAM1 and STAM2 are required for T-cell development and survival
- PMID: 12446783
- PMCID: PMC139881
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8648-8658.2002
Signal-transducing adaptor molecules STAM1 and STAM2 are required for T-cell development and survival
Abstract
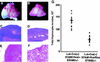
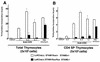
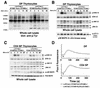
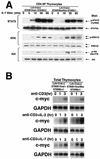
We previously reported that the STAM family members STAM1 and STAM2 are phosphorylated on tyrosine upon stimulation with cytokines through the gammac-Jak3 signaling pathway, which is essential for T-cell development. Mice with targeted mutations in either STAM1 or STAM2 show no abnormality in T-cell development, and mice with double mutations for STAM1 and STAM2 are embryonically lethal; therefore, here we generated mice with T-cell-specific double mutations for STAM1 and STAM2 using the Cre/loxP system. These STAM1(-/-) STAM2(-/-) mice showed a significant reduction in thymocytes and a profound reduction in peripheral mature T cells. In proliferation assays, thymocytes derived from the double mutant mice showed a defective response to T-cell-receptor (TCR) stimulation by antibodies and/or cytokines, interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-7. However, signaling events downstream of receptors for IL-2 and IL-7, such as activations of STAT5, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt, and c-myc induction, were normal in the double mutant thymocytes. Upon TCR-mediated stimulation, prolonged activations of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and Jun N-terminal protein kinase were seen, but activations of ERK, PKB/Akt, and intracellular calcium flux were normal in the double mutant thymocytes. When the cell viability of cultured thymocytes was assessed, the double mutant thymocytes died more quickly than controls. These results demonstrate that the STAMs are indispensably involved in T-cell development and survival in the thymus through the prevention of apoptosis but are dispensable for the proximal signaling of TCR and cytokine receptors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hrs, a mammalian master molecule in vesicular transport and protein sorting, suppresses the degradation of ESCRT proteins signal transducing adaptor molecule 1 and 2.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 18;280(11):10468-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409969200. Epub 2005 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15640163
-
Loss of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons in mice lacking STAM1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;21(11):3807-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.11.3807-3819.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11340172 Free PMC article.
-
STAM2, a new member of the STAM family, binding to the Janus kinases.FEBS Lett. 2000 Jul 14;477(1-2):55-61. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01760-9. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 10899310
-
IL-7: Comprehensive review.Cytokine. 2022 Dec;160:156049. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.156049. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 36201890 Review.
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of T cell development.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Feb;61(3):263-80. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3224-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 14770292 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Compilation of Human SH3 Domains: A Versatile Superfamily in Cellular Signaling.Cells. 2023 Aug 12;12(16):2054. doi: 10.3390/cells12162054. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESCRT-II/Vps25 constrains digit number by endosome-mediated selective modulation of FGF-SHH signaling.Cell Rep. 2014 Oct 23;9(2):674-87. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.019. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25373905 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the neuromuscular deficits caused by STAM1 deficiency.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2024 Aug 23;7:100138. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2024.100138. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39280771 Free PMC article.
-
PTP1B targets the endosomal sorting machinery: dephosphorylation of regulatory sites on the endosomal sorting complex required for transport component STAM2.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 30;285(31):23899-907. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115295. Epub 2010 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20504764 Free PMC article.
-
STAM adaptor proteins interact with COPII complexes and function in ER-to-Golgi trafficking.Traffic. 2009 Feb;10(2):201-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00856.x. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Traffic. 2009. PMID: 19054391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asao, H., Y. Sasaki, T. Arita, N. Tanaka, K. Endo, H. Kasai, T. Takeshita, Y. Endo, T. Fujita, and K. Sugamura. 1997. Hrs is associated with STAM, a signal-transducing adaptor molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32785-32791. - PubMed
-
- Boise, L. H., M. Gonzalez-Garcia, C. E. Postema, L. Ding, T. Lindsten, L. A. Turka, X. Mao, G. Nunez, and C. B. Thompson. 1993. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74:597-608. - PubMed
-
- Cao, X., E. W. Shores, J. Hu-Li, M. R. Anver, B. L. Kelsall, S. M. Russell, J. Drago, M. Noguchi, A. Grinberg, E. T. Bloom, et al. 1995. Defective lymphoid development in mice lacking expression of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain. Immunity 2:223-238. - PubMed
-
- Di Santo, J. P., I. Aifantis, E. Rosmaraki, C. Garcia, J. Feinberg, H. J. Fehling, A. Fischer, H. Boehmer, and B. Rocha. 1999. The common cytokine receptor chain and the pre-T cell receptor provide independent but critically overlapping signals in early α/β T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 189:563-574. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
